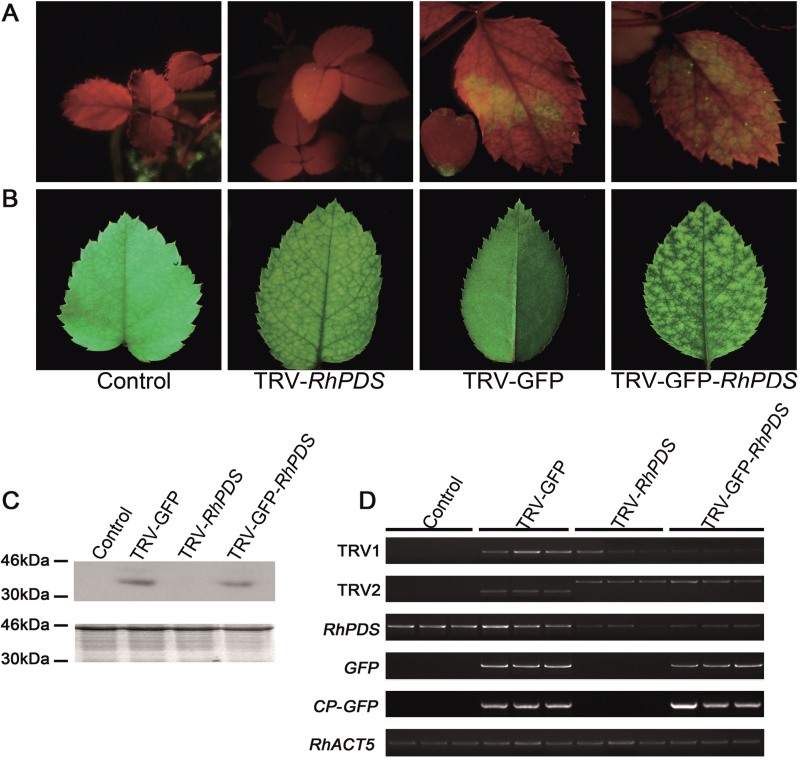
Fig. 7.
Silencing of RhPDS in rose seedlings. (A) TRV- and TRV–GFP-infiltrated rose plants. Rose seedlings were inoculated with a mixture of pTRV2-RhPDS/pTRV2-GFP-RhPDS and pTRV1 (1:1, OD600=1.0) using vacuum infiltration. The plants were photographed under UV illumination and normal light at 25 and 30 dpi, respectively. The inset image in the fluorescent photo of TRV–GFP-infected plant shows a petal with GFP green fluorescence. (B) CP–GFP protein levels in upper leaves 30 d after TRV vector inoculation. A 10 μg aliquot of protein was used for western blot in each lane and anti-GFP was used as antibody to detect CP–GFP fusion protein. Coomassie blue staining was used for confirmation of equal loading in each lane. (C) Semi-quantitative RT–PCR of TRV1, TRV2, RhPDS, GFP, and CP-GFP in control and inoculated plants. RhACT5 was used as an internal control. Total RNA and protein were extracted from the top young leaves.