Figure 2.
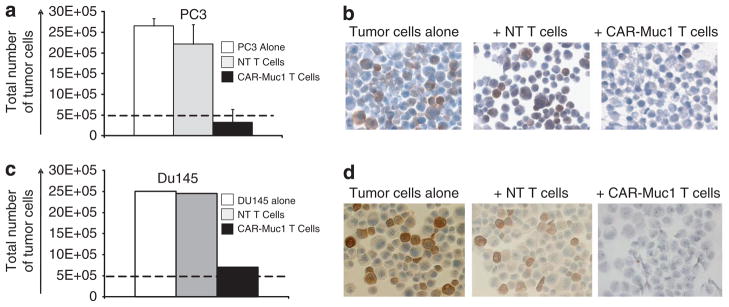
Tumor immune escape due to heterogeneous tumor antigen expression. (a) Shows that CAR-Muc1 T cells (■) kill the Muc1-expressing prostate cancer cell line PC3 while control NT T cells (
 ) have little impact on tumor cell growth. Untreated tumor cells (■) served as an additional control. Cytotoxic activity was evaluated in a 72-h co-culture experiment (ratio 1 tumor cell:10T cells) and results are shown as total number of residual tumor cells. Data represent the mean±s.d. of four donors. (b) Shows IHC analysis for Muc1 tumor antigen expression performed on tumor cells that were untreated (left panel), treated with control NT T cells (middle panel), or treated with CAR-Muc1 T cells (right panel). (c, d) Show similar results for a second prostate cancer cell line, DU145.
) have little impact on tumor cell growth. Untreated tumor cells (■) served as an additional control. Cytotoxic activity was evaluated in a 72-h co-culture experiment (ratio 1 tumor cell:10T cells) and results are shown as total number of residual tumor cells. Data represent the mean±s.d. of four donors. (b) Shows IHC analysis for Muc1 tumor antigen expression performed on tumor cells that were untreated (left panel), treated with control NT T cells (middle panel), or treated with CAR-Muc1 T cells (right panel). (c, d) Show similar results for a second prostate cancer cell line, DU145.
