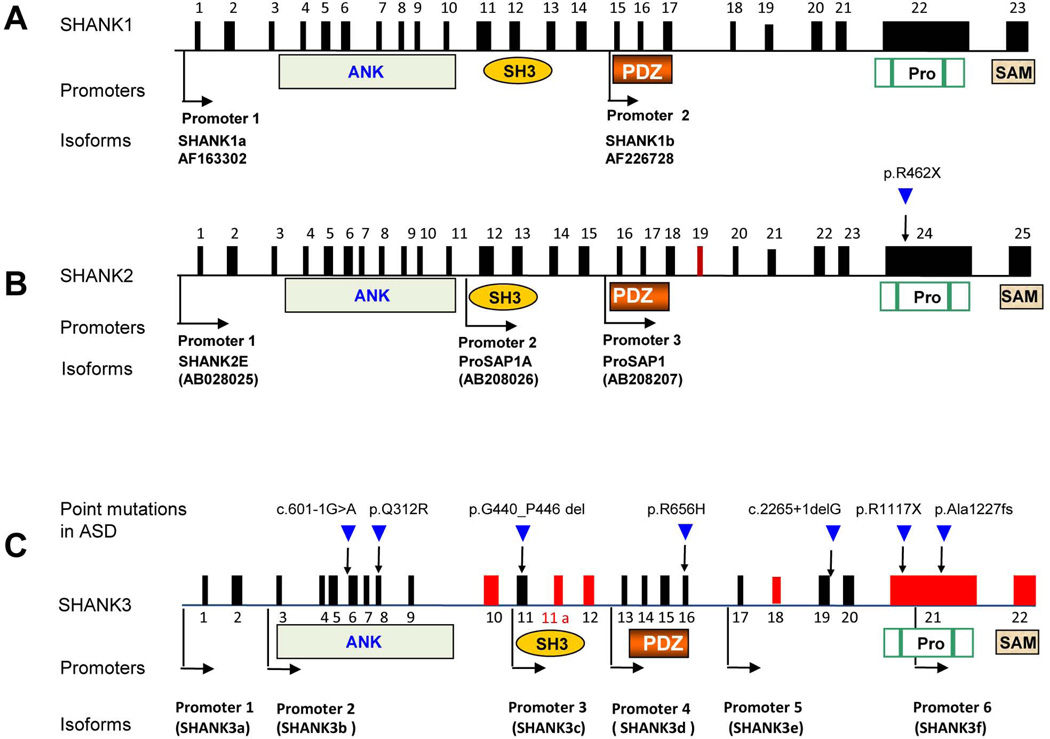
Figure 1. SHANK family gene structure, mutations, and protein domains.
The gene structures are deduced from cDNAs of AF163302 for SHANK1, AB208205 for SHANK2, and AB569469 for SHANK3 deposited in GenBank. The promoters are shown in arrows and the alternatively spliced exons are indicated in red. Microdeletions of SHANK1, SHANK2, and SHANK3 and point mutations of SHANK2 and SHANK3 are reported in ASD. Exon 11a of SHANK3 is a newly identified exon. The positions of six identified promoters are indicated as black arrows. The exons in red are alternatively spliced. The positions of point mutations are indicated as blue arrows and the nature of point mutations are as described above the arrow. c.601-1G>A splicing mutation in intron 5 (Hamdan et al., 2011), p.Q312R in exon 8 (Moessner et al., 2007), p.G440_P446del in exon 11 (Waga et al., 2011), p.R656H in exon 16 (Waga et al., 2011), c.2265+1delG splicing mutation in intron 19 (Gauthier et al., 2009), p.R1117X (Gauthier et al., 2010) and p.Ala1227fs in exon 21 (Durand et al., 2007). Protein domains are shown and aligned to corresponding exons (Pro, proline rich region).