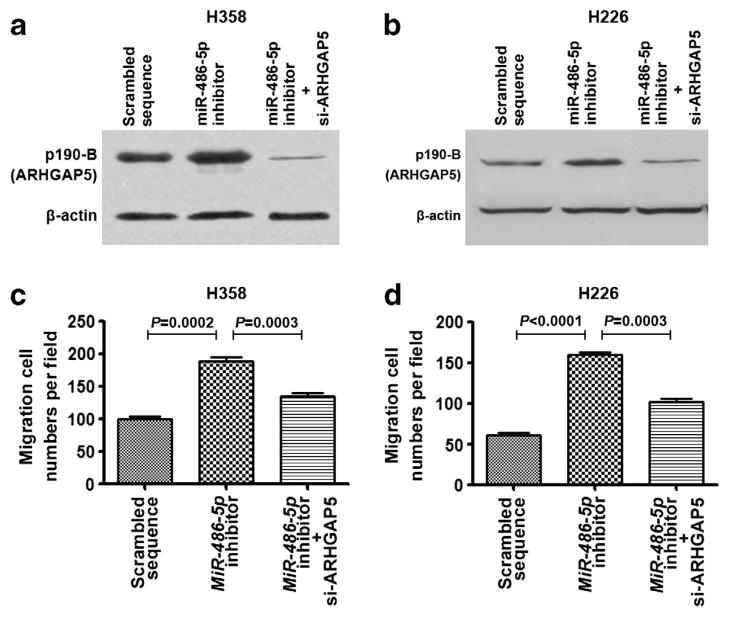
Figure 6.
ARHGAP5 is involved in miR-486-5p-induced suppression of cell migration and invasion of NSCLC. (a) H358 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor and si-ARHGAP5 exhibited reduced ARHGAP5 expression, whereas H358 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor had increased ARHGAP5 expression determined by western blotting with p190-B antibody. (b) H226 cells transfected with miR-486-5p inhibitor and si-ARHGAP5 had reduced ARHGAP5 expression, whereas H226 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor showed elevated ARHGAP5 expression. (c) H358 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor and si-ARHGAP5 had reduced migration and invasion potential, whereas H358 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor displayed increased potential of migration and invasion determined by Transwell assay. (d) H226 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor and si-ARHGAP5 had reduced migration and invasion potential, whereas H226 cells treated with miR-486-5p inhibitor showed elevated potential of migration and invasion.