Fig. 1.
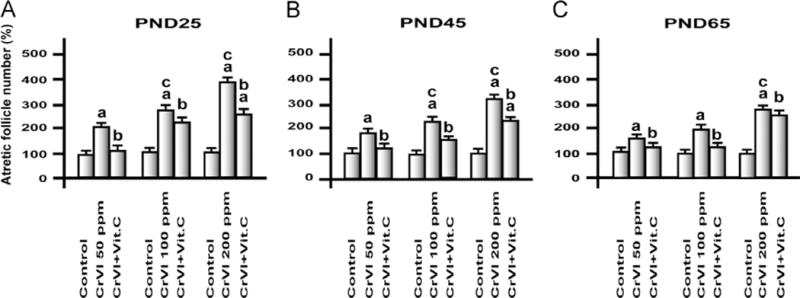
Effects of lactational exposure to CrIII on follicular atresia of F1 offspring. Experimental details are described under Materials and methods. Lactating mother rats received 50, 100, or 200 ppm CrVI in drinking water, with or without vitamin C supplementation through gavage. Suckling F1 female offspring received CrIII through mother’s milk during PNDs 1–21. After PND 21 pups from both control and treatment groups were continued on regular diet and water and were euthanized on PND 25. Ovaries were fixed, embedded, and serially sectioned, and every 12th section was used for counting atretic follicles, and the remaining unstained sections were used for TUNEL assay. aControl vs CrVI or CrVI+vitamin C; bCrVI vs CrVI+vitamin C; cCrVI 50 ppm vs CrVI 100 ppm or CrVI 200 ppm. Each value represents the mean±SEM of 20 rats, P<0.05.
