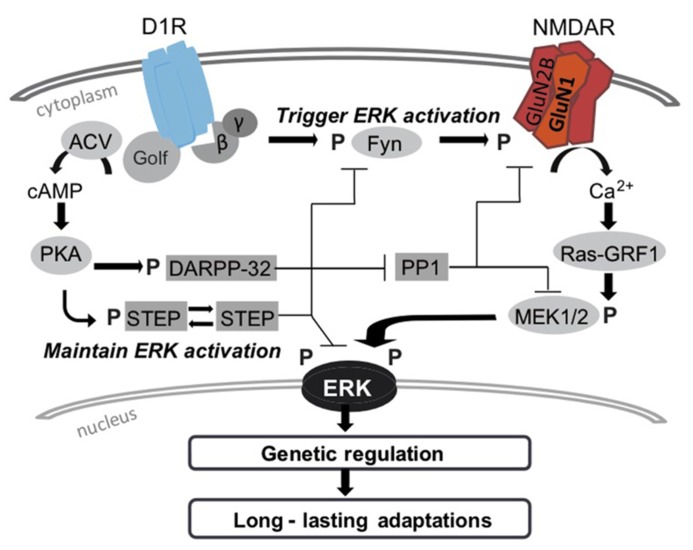
FIGURE 1.
Cocaine, similarly to most drugs of abuse, produces long lasting brain changes, that relie on gene expression and new protein synthesis. These long-term neuronal adaptations take place in majority in DA-D1R expressing MSNs that belong to the direct pathway. The ERK pathway is central in this striatal plasticity, and detects a combination of glutamate and DA signals that are essential for long lasting modifications. Cocaine-induced ERK activation depends on complex cascade of phosphorylation events downstream D1-R. Importantly, the triggering event in ERK activation depends on a non-canonical signaling pathway that associates Fyn-induced phosphorylation of GluN2B and increases in calcium influx into D1-R MSNs. The duration and maintenance of ERK activation occurs via cAMP/PKA pathway. The cAMP/PKA pathway, downstream D1 receptors (left panel) triggers deactivation of phosphatases, PP1 on one hand via DARPP-32, and STEP on the other hand (Valjent et al., 2005). By controling the activity of the tyrosine kinase Fyn and the dual specificity protein kinase MEK, this signaling cascade intervenes in the state of phosphorylation of ERK downstream DA-D1R stimulation. However, we propose that triggering ERK activation depends on a “non-canonical signaling” pathway downstream D1-R (right panel). A cAMP-independent activation of Fyn produces tyrosine phosphorylation of GluB2B subunit of NMDA-Rs that in turn facilitates calcium influx (Pascoli et al., 2011a), and activation of the calcium-sensitive Ras-guanine releasing factor (Ras-GRF1) that activates the MEK/ERK pathway (Fasano and Brambilla, 2011). Upon cocaine stimulation ERK translocates to the nucleus where it controls epigenetic and genetic programs. Among the latter, the transcription factor Elk-1 is a component of the ternary complex factor, which binds to SRE (Besnard et al., 2011a). ERK1/2 also phosphorylates the nuclear kinase MSK1which appears to play a prominent role in phosphorylation of histone H3 and cAMP-response element-binding (CREB) protein (Brami-Cherrier et al., 2005). This leads to the expression of immediate-early genes, which are particularly sensitive to CREB (e.g., cFos) or ternary complex factor (e.g., Zif268 a.k.a. Egr-1). These two nuclear pathways downstream from ERK have distinct roles in long-term behavioral adaptations (see text). DA-GPCR and NMDAR, in particular D1R and GluN1, oligomerization has been documented in heterologous systems, hippocampal, and striatal tissues after cocaine exposure. The role of D1R-GluN1 interaction in ERK activation and downstream molecular events remains to be established.