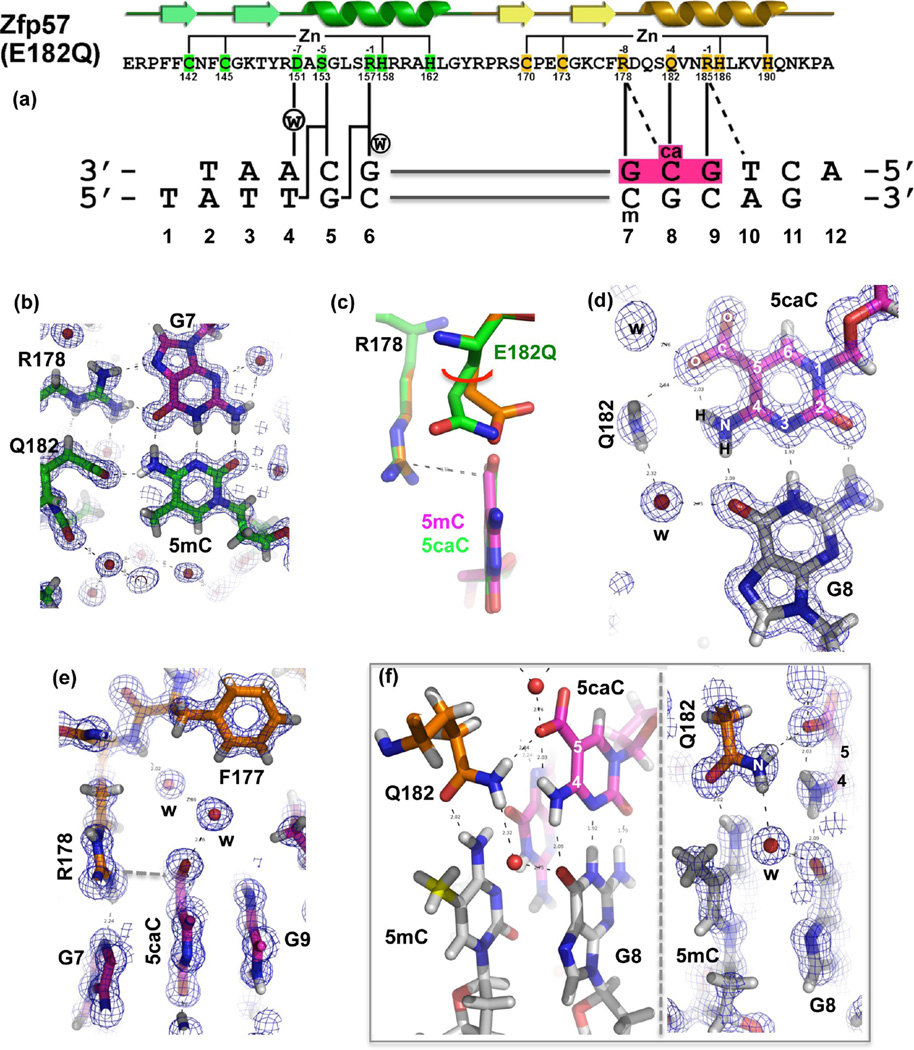
Figure 3.
Atomic structure of Zfp57 E182Q in complex with 5caC DNA. (a) The secondary structure elements (arrows for β-strands and ribbons for α-helices) are shown above the protein sequence. The amino acid positions highlighted are responsible for Zn ligand binding (C2H2) and DNA base-specific interactions (−1 to −8 relative to the first Zn-binding His). (b) Details of E182Q base-specific interactions for the 5mC:G base pair. Electron densities (2Fo − Fc) contoured at 1σ above the mean are shown. (c) Structural comparison of Zfp57 WT (orange) and the E182Q mutant (green) interacting with 5mC and 5caC, respectively. (d) Details of E182Q base-specific interactions for the 5caC:G base pair. (e) Arg178 forms an ion pair with the carboxylate moiety of 5caC. (f) The side chain of Gln182 links 5caC (via the amide group) of the top strand to 5mC (via the carbonyl oxygen) of the bottom strand. The left panel illustrates interactions of Gln182 with the CpG duplex, and the right panel shows a superimposition with the electron density.