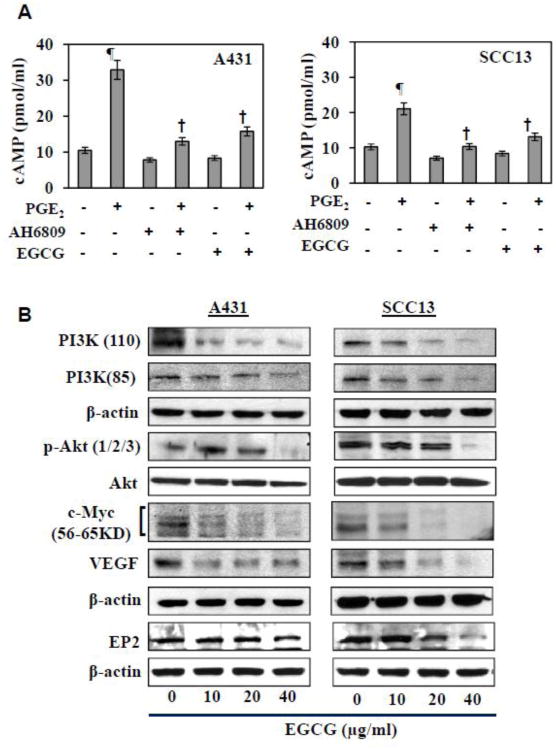
Figure 4.
Effect of EGCG on cyclic AMP and cell survival signaling proteins in A431 and SCC13 skin cancer cells. (A) Treatment of skin cancer cells with either EP2 receptor antagonist (10 μM) or EGCG (40 μg/ml) inhibits PGE2 (10 μM)-induced expression of cAMP. Significant increase vs control, ¶P<0.001; significant decrease vs PGE2-treated cells, †P<0.001. (B) EGCG treatment inhibits the levels of cell survival signaling proteins (proteins of PI3K pathway) and its downstream targets, such as c-Myc and VEGF, in skin cancer cells. Cells were treated with various concentrations of EGCG for 48 h, and cell lysates were subjected to the analysis of various proteins using western blot analysis. Equal loading of proteins on gel was verified after probing the stripped membrane with anti β-actin antibody.