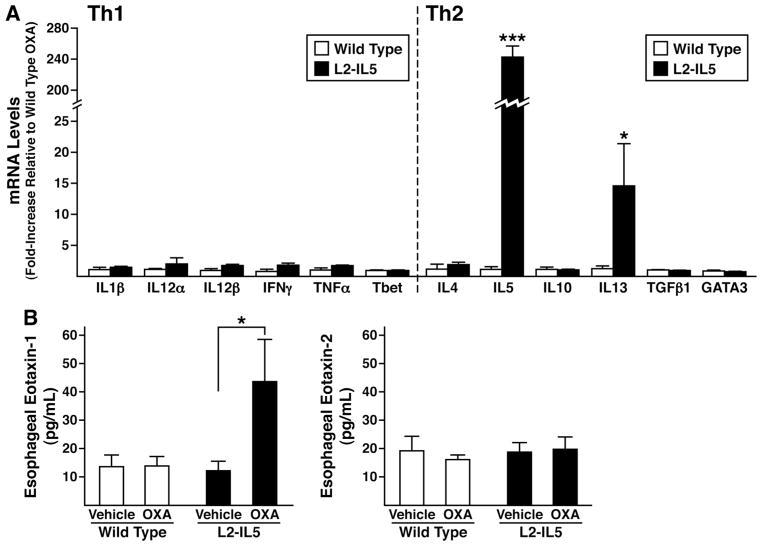
Figure 7.
The induced eosinophilic oesophageal inflammation occurring in 4-ethoxymethylene-2-phenyl-2-oxazolin-5-one (OXA)-treated L2-IL5 mice is characterised by a T-helper cell (Th) type 2 predominated cytokine expression profile accompanied by overexpression of the eosinophil agonist chemokine eotaxin-1 but not eotaxin-2. (A) Total RNA derived from whole oesophagi of OXA-treated wild-type versus L2-IL5 mice were used as the starting templates for Taqman based real-time reverse-transcription PCR assessments of expression from genes encoding cytokines characteristic of Th1 versus Th2 immune responses. Expression levels were normalised within each group relative to the levels of 18S ribosomal RNA before determination of fold increase relative to observed levels in the oesophagi of OXA-treated wild-type mice. Individual values are expressed as group means±SEM *p≤0.05, ***p≤0.001. (B) Eotaxin-1 and 2 expression levels derived from the oesophagi of each group of mice were determined by ELISA of supernatants derived from explants cultured for 24 h. These data are representative of two separate experiments and are shown as mean values±SEM of three to five individual mice per group. *p≤0.05, ***p≤0.001.