Figure 1.
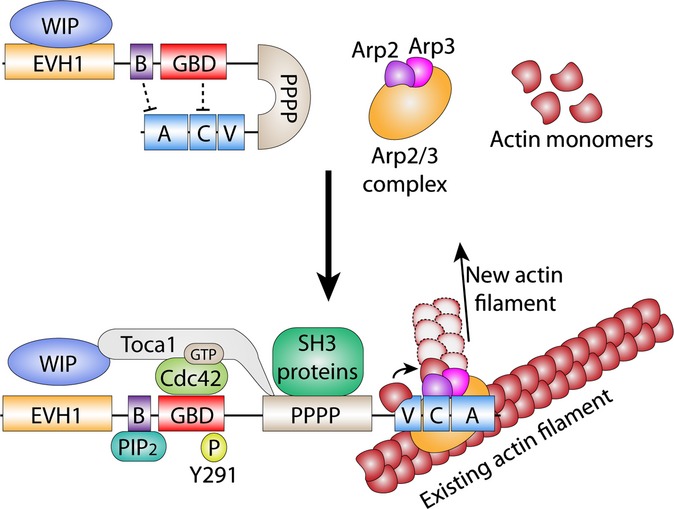
WASp domain structure, interacting proteins, and activation. Cytosolic WASp exists in an auto-inhibited conformation, with the VCA domain tethered to the GBD and basic domains. This inactive state is stabilized by WIP binding to the EVH1 domain. WASp is activated by a variety of signals, including GTP-Cdc42, PIP2, and Y291 phosphorylation by SH3 kinases recruited by the polyproline domain. Toca1 aids WASp activation by displacing WIP, binds GTP-Cdc42, and is required for PIP2 activation of WASp. Activation is restricted to the cell cortex where PIP2 and GTP-Cdc42 are present. Upon activation, the VCA domain is free to bind to and activate Arp2/3. Active Arp2/3 then attaches to an existing actin filament, where Arp2 and Arp3 form the template for a new actin filament branched at a 70° angle from the parent filament.
