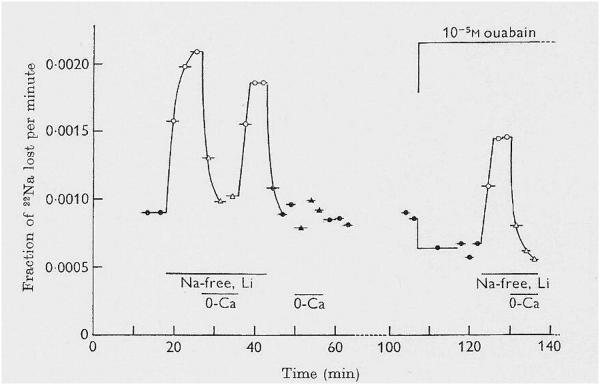
Figure 1.
Reduction of [Na+]o activates a large Cao-dependent, ouabain-resistant 22Na+ efflux in squid axons with high [Na+]i. Replacement of 460 mM NaCl in the artificial sea water (ASW) by LiCl greatly increased 22Na+ efflux, measured as the fraction of 22Na+ lost per minute. The increment was abolished by removal of the 11 mM CaCl2 in the ASW (MgCl2 was increased from 55 to 66 mM). This is evidence of “Nao-Cao antagonism”, and indirect evidence for Na+/Ca2+ exchange. Ouabain (10−5 M) reduced the 22Na+ efflux in control Na ASW (i.e., it inhibited the Na+ pump), but it had no effect on the large Cao-dependent 22Na+ efflux in Li ASW; right). Reprinted from Baker et al., 1969, with permission.