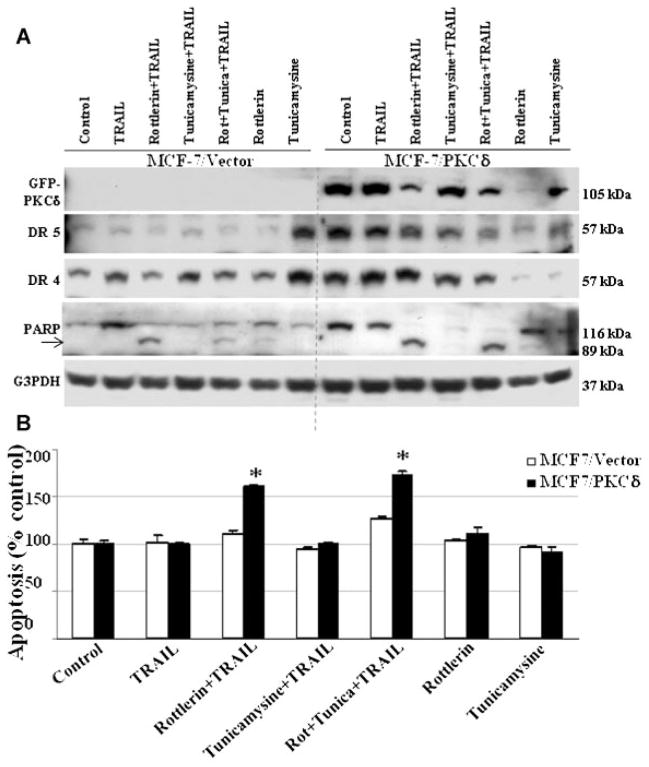
Fig. 2.
A: PKCδ overexpression protects the MCF-7 cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis. MCF-7 cells overexpressing PKCδ (MCF-7/PKCδ) or vector alone (MCF-7/vector) were treated with TRAIL (10 ng/ml), rottlerin (3 μM), tunicamycin (10 μg/ml) alone, or in combination with TRAIL for 4 h. After 4 h PKCδ, DR4, DR5, and PARP cleavage were evaluated using specific antibodies by Western blots. MCF-7/PKCδ cells showed enhanced DR4 and DR5 expression in comparison to vector-transfected control cells. However, addition of TRAIL was unable to induce a significant increase in PARP cleavage in comparison to controls. Combination of TRAIL and rottlerin (PKCδ inhibitor) significantly enhanced PARP cleavage. Equivalent protein loading was assessed by stripping the membrane and re-probing with G3PDH antibody. Arrow indicates cleaved fragment. B: PKCδ inhibition enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Inhibition of PKCδ by rottlerin (3 μM) enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Apoptosis was quantified by ELISA and normalized to values measured in untreated cells. MCF-7/PKCδ cell showed a significant increase in TRAIL-induced apoptosis in the presence of rottlerin in comparison to untreated cells ((P <0.001). Data are mean +SE of triplicate determinations.