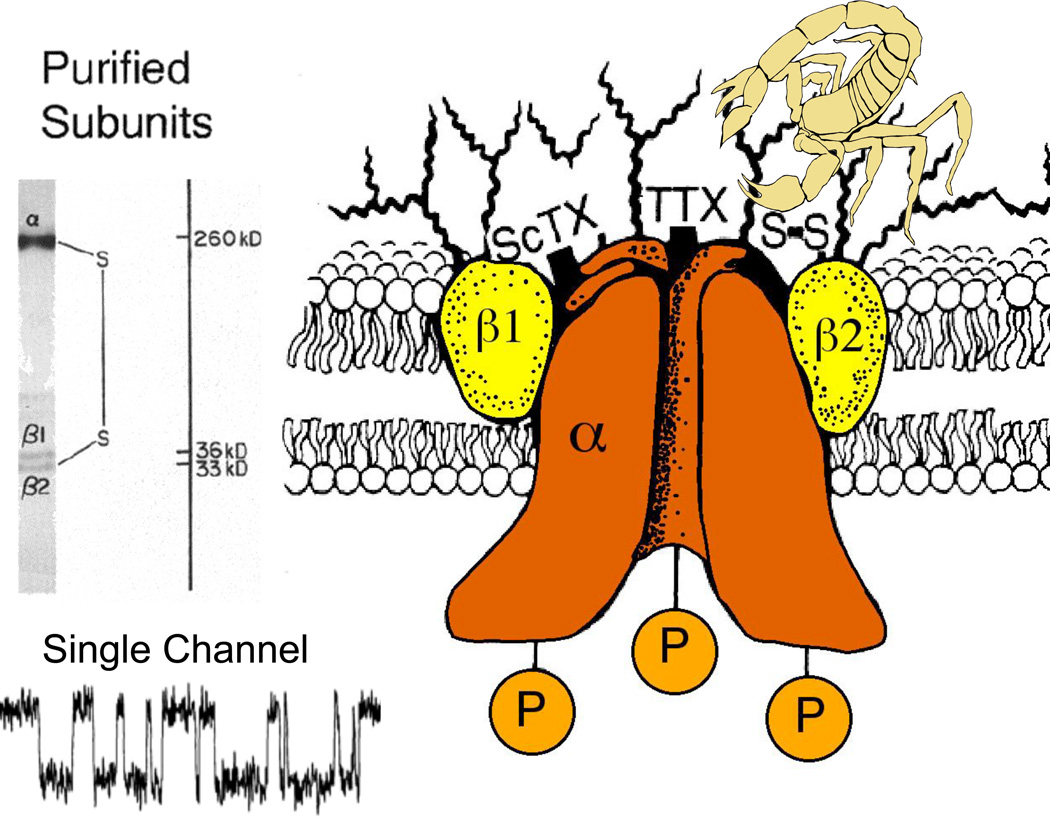
Figure 1. Subunit structure of voltage-gated sodium channels.
A. SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis patterns illustrating the α and (β subunits of the brain sodium channels. Left. α and (βi subunits covalently labeled with [ 125 I]-labeled scorpion toxin (Beneski and Catterall, 1980). Lane 1, specific labeling; lane 2, nonspecific labeling. Right. Sodium channel purified from rat brain showing the α, β1, and β2 subunits and their molecular weights (Hartshorne et al., 1982). As illustrated, the α and β2 subunits are linked by a disulfide bond. Tetrodotoxin and scorpion toxins bind to the α subunits of sodium channels as indicated and were used as molecular tags to identify and purify the sodium channel protein (Beneski & Catterall, 1980; Hartshorne et al., 1982; Hartshorne & Catterall, 1984). Inset. Single channel currents conducted by a single purified sodium channel incorporated into a planar bilayer (Hartshorne et al., 1985).