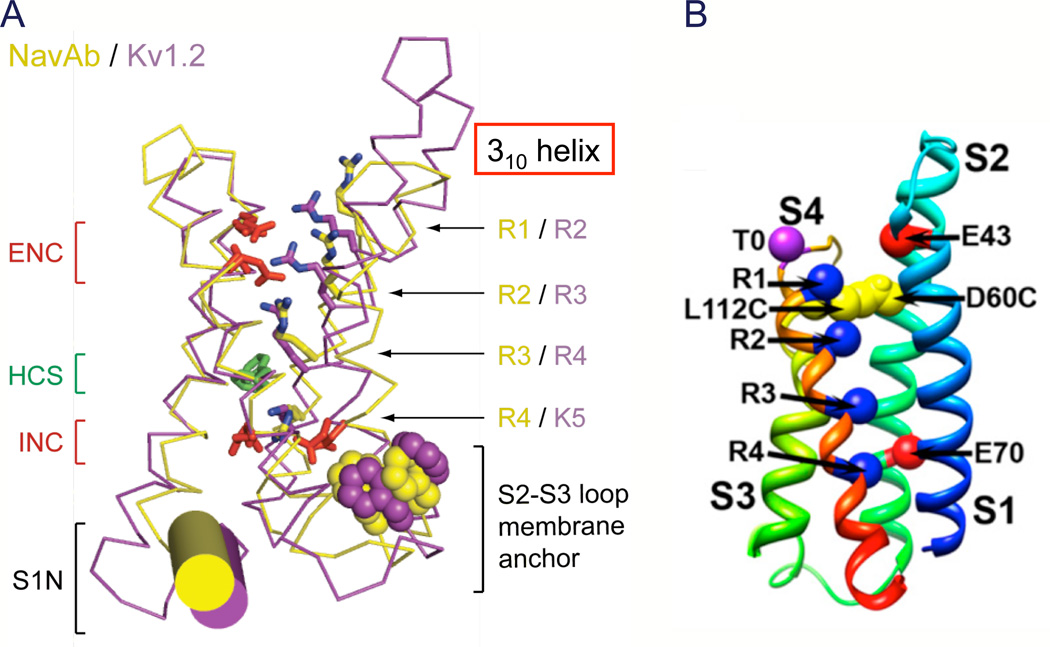
Figure 4. Structure of the voltage sensor.
A. Structure of the voltage sensor in an activated state. Side views of the structures of NaVAb(yellow (Payandeh et al., 2011)) and KV1.2 (purple (Long et al., 2005a)) are superimposed. Extracellular negative cluster (ENC), red; hydrophobic constriction site (HCS), green; intracellular negative cluster (INC), red. B. Model of the resting state of the NaChBac voltage sensor. Gating charges R1–R4, blue; T0, Thr in the position of the R0 gating charge in some KV channels. L112C, Cys substituted for Leu adjacent to R1 in S4 segment forming a disulfide bond with Cys substituted for Asp60 (D60C) in S2 segment in the resting state as observed in disulfide locking experiments. E43, Glu 43 in S1 segment, a component of the extracellular negative cluster. E70, Glu70 in S2 segment, a component of the intracellular negative cluster.