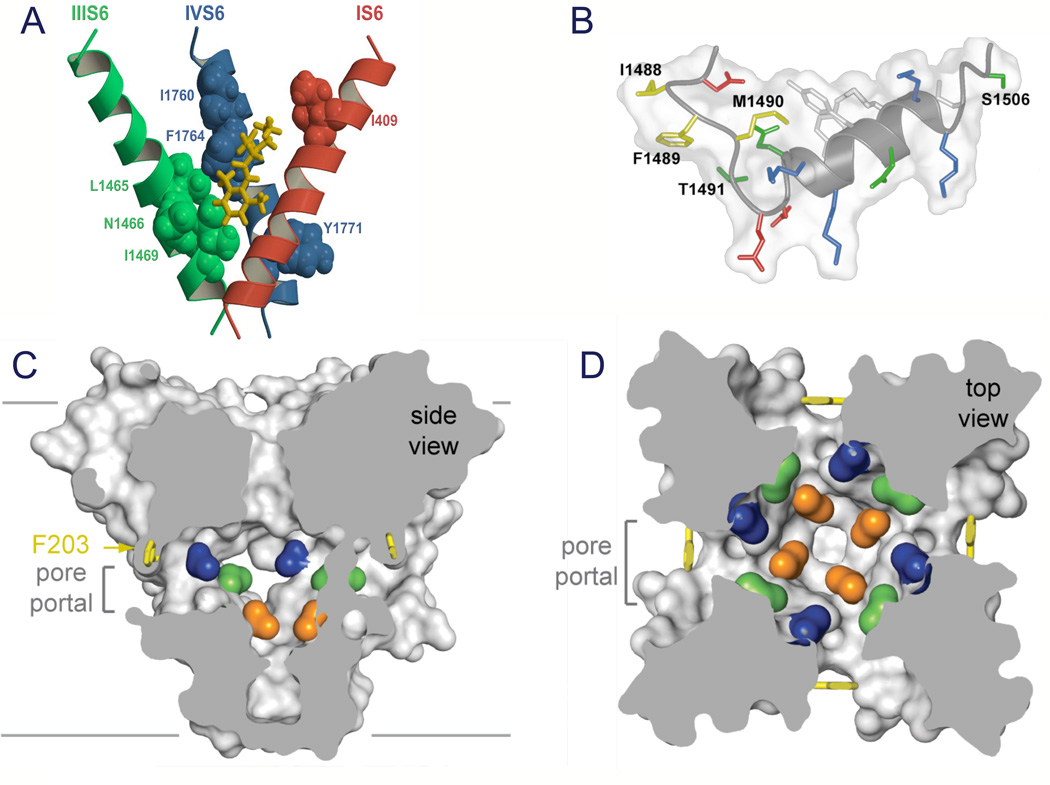
Figure 9. Drug receptor site and fast inactivation gate.
A. Model of the local anesthetic receptor site in mammalian NaV1.2 channels (Yarov-Yarovoy et al., 2002). B. Structure of the inactivation gate of mammalian NaV1.2 channels in solution determined by NMR (Rohl et al., 1999). C. Side-view through the pore module illustrating fenestrations (portals) and hydrophobic access to central cavity. Phe203 side-chains, yellow sticks. Surface representations of NaVAb residues aligning with those implicated in drug binding and block, Thr206, blue; Met209, green; Val213, orange. Membrane boundaries, grey lines. Electrondensity from an Fo-Fc omit map is contoured at 2.0 σ. D. Top-view sectioned below the selectivity filter, colored as in C (Payandeh et al., 2011).