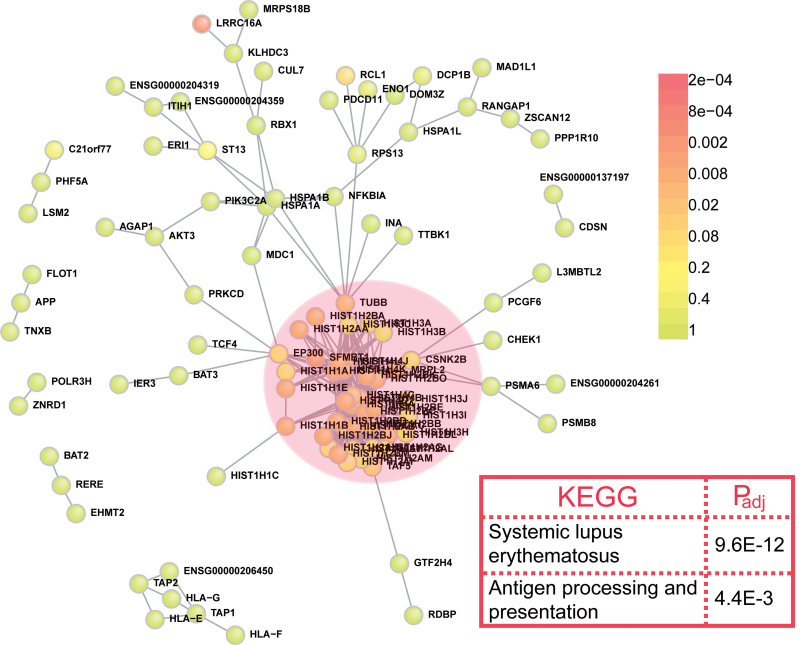
Fig. 1.
Proteins encoded by genes that were defined by the top 81 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from Schizophrenia Psychiatric Genome-Wide Association Study Consortium (PGC) form a highly significant interconnected network. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network constructed by genes that defined by top 81 SNPs from Schizophrenia PGC. There were 104 disease proteins participating in the direct network and 343 direct interactions in total. This degree of interconnectivity is statistically highly significant (P = 9.9 × 10− 4, corrected) compared with 10 000 random networks, which only have the 206 direct edges count expected by chance. The core of this highly interconnected network is composed of genes that are involved in nucleosome assembly (pink circle), suggesting an enrichment of nucleosome assembly genes in schizophrenia susceptibility loci. KEGG pathway analysis of the genes that participate in the direct network is shown in the red box. P values were corrected by the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure in DAVID.