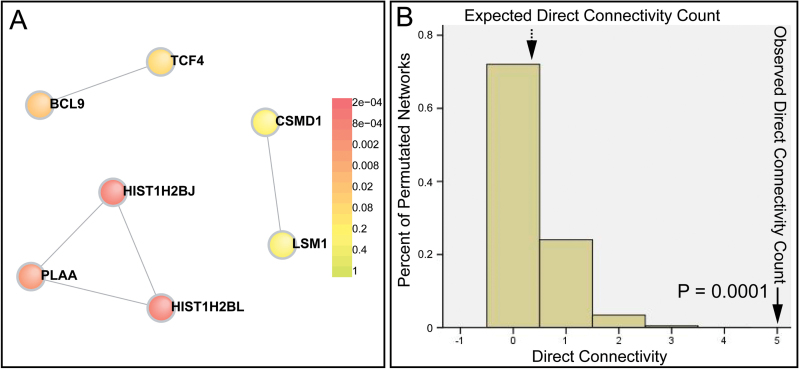
Fig. 2.
Protein products encoded by genome-wide significant schizophrenia susceptibility genes significantly interacted. (A) Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network constructed with genes that were significantly associated with schizophrenia in recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of schizophrenia. (B) Significant network (P = .0001) compared with 10 000 random networks, suggesting significant physical interactions between protein products of top schizophrenia susceptibility genes. Structurally equivalent random networks were built from a within-degree node-label permutation method. An empirical distribution was constructed for a direct connectivity count and used to assess the significance of networks. Numbers on the x-axis represent the direct network connectivity (the number of edges in the direct network), which were enumerated for the disease networks and 10 000 random networks. The plotted histogram represents random expectation (the dashed arrowhead), and the solid arrowheads indicate the schizophrenia network (observed). The y-axis represents percent of permutated networks (eg, the percentage of networks with 5 edges in the direct network is 0.0001, which is statistically significant compared with 10 000 random networks).