Figure 2.
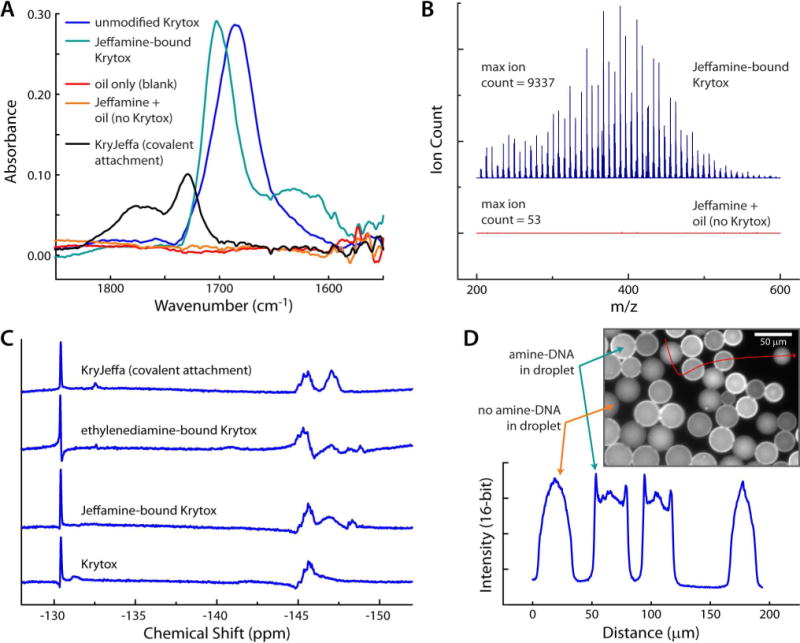
Evidence of direct binding. (A) FT-IR evidence of Jeffamine/Krytox interaction and comparison to the covalently-modified product, KryJeffa (black trace). (B) ESI-MS showed that Jeffamine extraction into HFE 7500 oil was dependent upon the presence of Krytox in the oil. (C) NMR spectra of the starting material (Krytox; bottom trace), Jeffamine-bound Krytox (second from bottom), ethylenediamine-bound Krytox (third from bottom), and the covalently-modified surfactant, KryJeffa (top trace). Primary amine bound Krytox spectra show distinct patterns different from both the starting material and the covalent product. (D) Fluorescence microscopy shows that amine-labeled DNA collects at the oil-water interface, while non-amine-labeled DNA is evenly dispersed.
