Figure 8. L-type VGCC subtypes contribute to calcium signalling in ganglion cell axons.
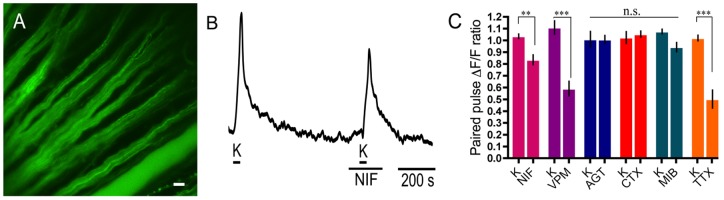
A. Fluo-4 labelling of RGC axons in the wholemount retina. Scale bar is 20 µm. B. Application of nifedipine (NIF; 10 µM), an L-type Ca channel antagonist, reduced the second high K+-evoked calcium signal. C. Summary of Ca2+ imaging results from RGC axons showing the following changes in paired pulse Ca2+ signal in response to drugs (applied during the second K+ pulse) compared to their control paired K+ pulses (K): 10 µM nifedipine (20%±6%; p = 0.0053; n = 12), 100 µM verapamil (VPM; 52%±9%; p<0.0001; n = 9) and 200 nM TTX (52%±11%; p = 0.0009; n = 8). 400 nM ω-agatoxin IVA (AGT; n = 9), 3 µM ω-conotoxin-GVIA (CTX; n = 7) and 3 µM mibefradil (MIB; n = 12) did not change the calcium signal in a statistically significant manner.
