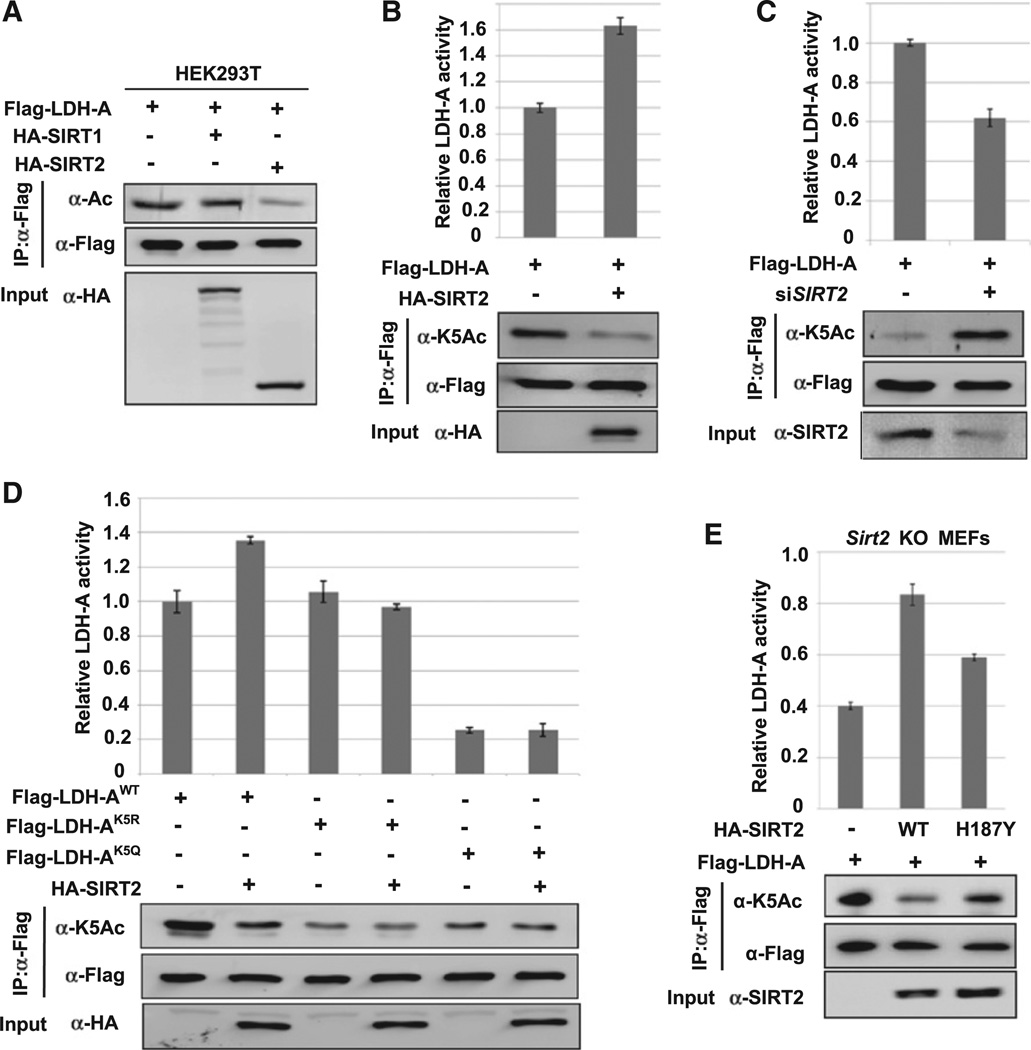
Figure 2. SIRT2 Deacetylates LDH-A at K5 and Increases LDH-A Activity.
(A) SIRT2 overexpression decreases LDH-A acetylation. 293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids and LDH-A acetylation was determined by western blotting.
(B) SIRT2 decreases K5 acetylation and increases LDH-A activity. 293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids, Flag-LDH-A was immuno-precipitated, and LDH-A activity was assayed. LDH-A activity was normalized against protein levels. Relative enzyme activities of triplicated experiments ± SD are presented.
(C) SIRT2 knockdown increases K5 acetylation and decreases LDH-A activity. 293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids and SIRT2 siRNA oligonucleotides. LDH-A was immunoprecipitated and activity was assayed. LDH-A acetylation at K5 was determined by western blotting. Relative enzyme activities of triplicate experiments ± SD are presented.
(D) SIRT2 overexpression increases the activity of wild-type, but not acetylation-deficient K5R or K5Q mutant LDH-A. 293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids, followed by immunoprecipitation and enzyme assay. Relative enzyme activities of triplicate experiments ± SD are presented.
(E) The deacetylase activity of SIRT2 is required to increase LDH-A activity. Sirt2 knockout MEFs were co-transfected with Flag-LDH-A and SIRT2 wild-type or the inactive mutant (H187Y). LDH-A was immunoprecipitated and enzyme activity was assayed. LDH-A activity was normalized against protein levels. Relative enzyme activities of triplicate experiments ± SD are presented.
See also Figure S2.