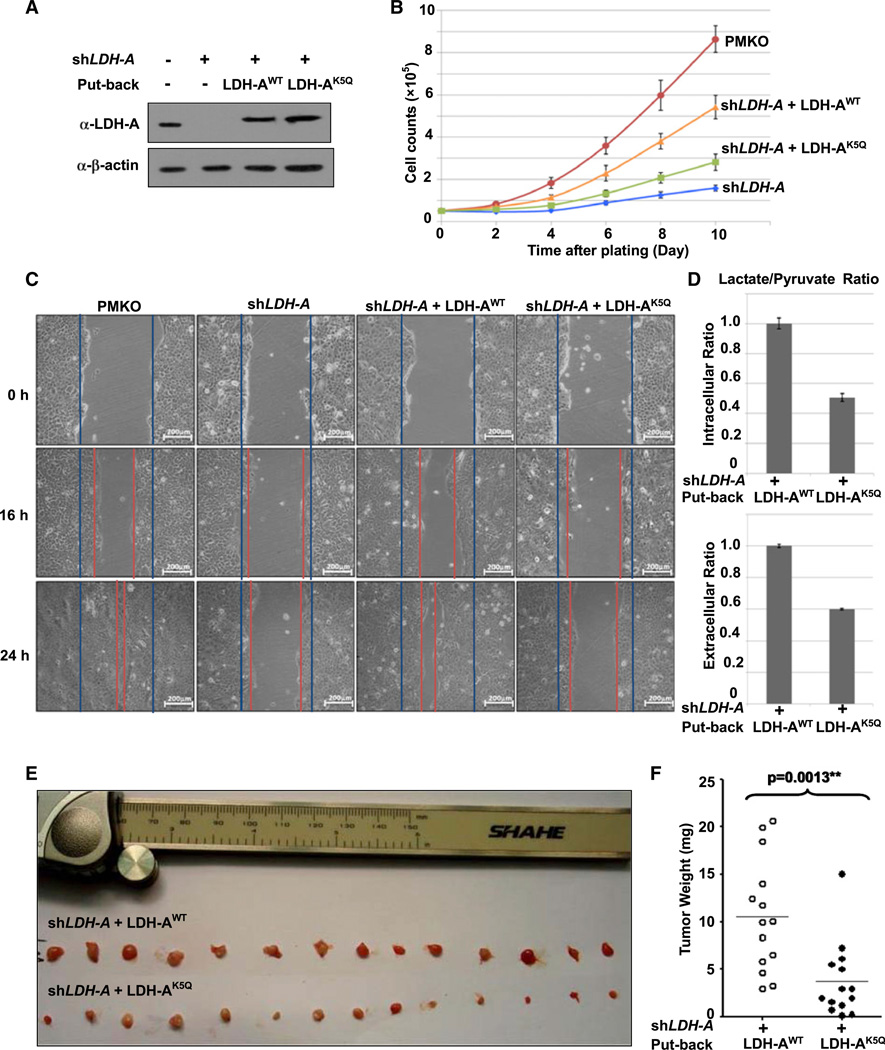
Figure 5. Acetylation Mimetic LDH-AK5Q Mutant Has Reduced Ability to Support Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration.
(A) Generation of LDH-A-expressing BxPC-3 stable cell lines. BxPC-3 cells stably knockdown LDH-A and re-express the shRNA-resistant wild-type or K5Q mutant were established. LDH-A knockdown efficiency and re-expression were determined by western blotting.
(B) LDH-AK5Q is compromised to support cell proliferation. LDH-AWT or LDH-AK5Q cells were seeded in each well. Cell numbers were counted every 48 hr. Error bars represent cell numbers ± SD for triplicate experiments.
(C) LDH-AK5Q mutant is compromised to support cell migration. BxPC-3 cells as described in panel A were analyzed for migration by a wound-healing assay. Scale bars are 200 mm.
(D) LDH-AK5Q decreases intracellular and extracellular lactate/pyruvate ratio. LDH-AWT or LDH-AK5Qcells were seeded in each well. Intracellular or extracellular pyruvate and lactate production were measured according to manufacturer’s protocol (BioVision). Error bars represent ± SD for triplicate experiments.
(E and F) LDH-AK5Q is defective in supporting tumor growth in vivo. Xenograft was performed using the BxPC-3 stable cell lines with LDH-A knockdown and re-expression of shRNA-resistant wild-type or K5Q mutant LDH-A as indicated. Seven weeks later, mice were sacrificed and tumor weight was measured. The p value was calculated by paired t test. See also Figure S5.