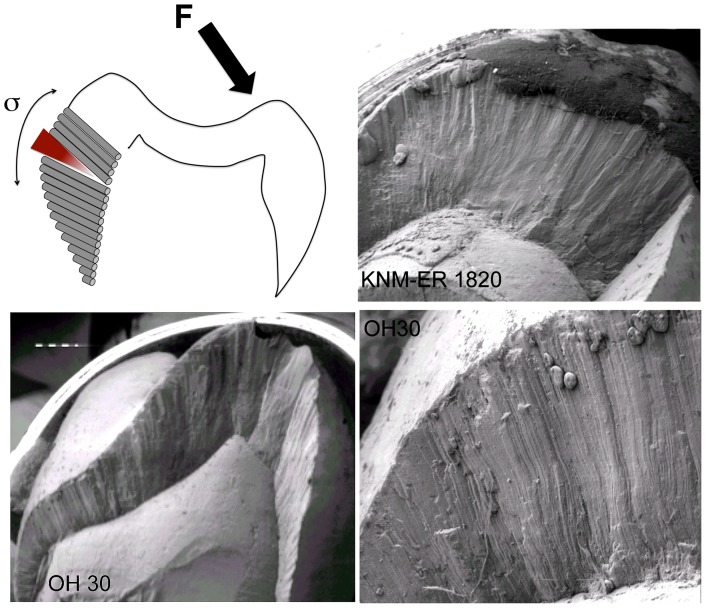
Figure 2. Illustration of the tensile stresses (σ) and resulting breakages in P. boisei teeth.
Tensile stresses (σ) would occur when lateral loads are applied to a straight-walled tooth and the force vector is directed outside the dental tissue. Without decussating enamel, i.e. bundels of enamel prisms crossing over, transverse cracks initiated on the unloaded side will propagate through the tissue and will lead to catastrophic failure of the tooth. Cracks tend to travel along the protein-rich prism sheaths and are stopped by differently-oriented prisms. Such oblique/transverse breakages are frequently found in P. boisei teeth and are illustrated here in a sample of SEM pictures. Although these breaks may have occurred post mortem, they illustrate the plane of least resistance and thus allow an assessment of the loading conditions to which the tooth should not have been subjected in vivo. Images are not to scale and are for illustration only.