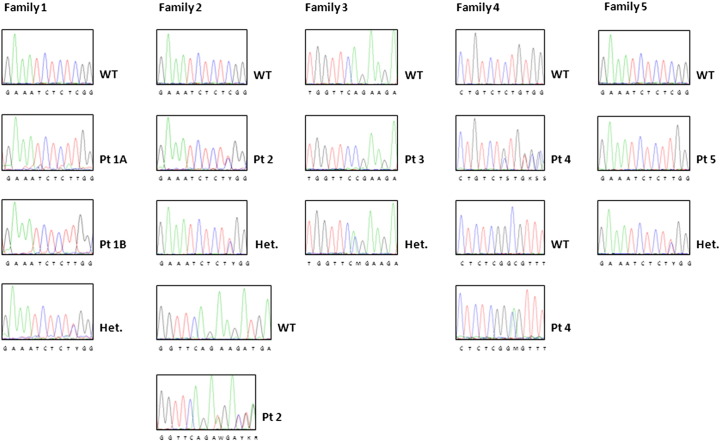
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Molecular findings in 6 new CTSK-dependent patients.
Family 1: A homozygous single nucleotide change (g.2128C > T) causing an Arg46Trp change was identified in the two affected siblings; this mutation was present in the parents at the heterozygous state (see lowest chromatogram in this series).
Family 2: Patient 2 was a compound heterozygote for the nucleotide change above described (present also in the paternal DNA at the heterozygous state) and a deletion of 3 nucleotides (g.2343_2345del), leading to the deletion of a single residue (p.Lys89del).
Family 3: A homozygous transversion (g.2340A > C) causing a Gln88Pro change was identified in the patient; this mutation was present in the parents at the heterozygous state (see lowest chromatogram).
Family 4: Patient 4 was a compound heterozygote for a single nucleotide (g.2131C > A), causing an Arg47Ser substitution, and a deletion of 2 nucleotides (g.8746_8747del), causing a frameshift and a premature protein termination (p.Ser246CysfsX4).
Family 5: The same single nucleotide change found in the patients 1A, 1B and 2 was present at the homozygous state in Patient 5 and at the heterozygous state in his parents (see lowest chromatogram in this series).