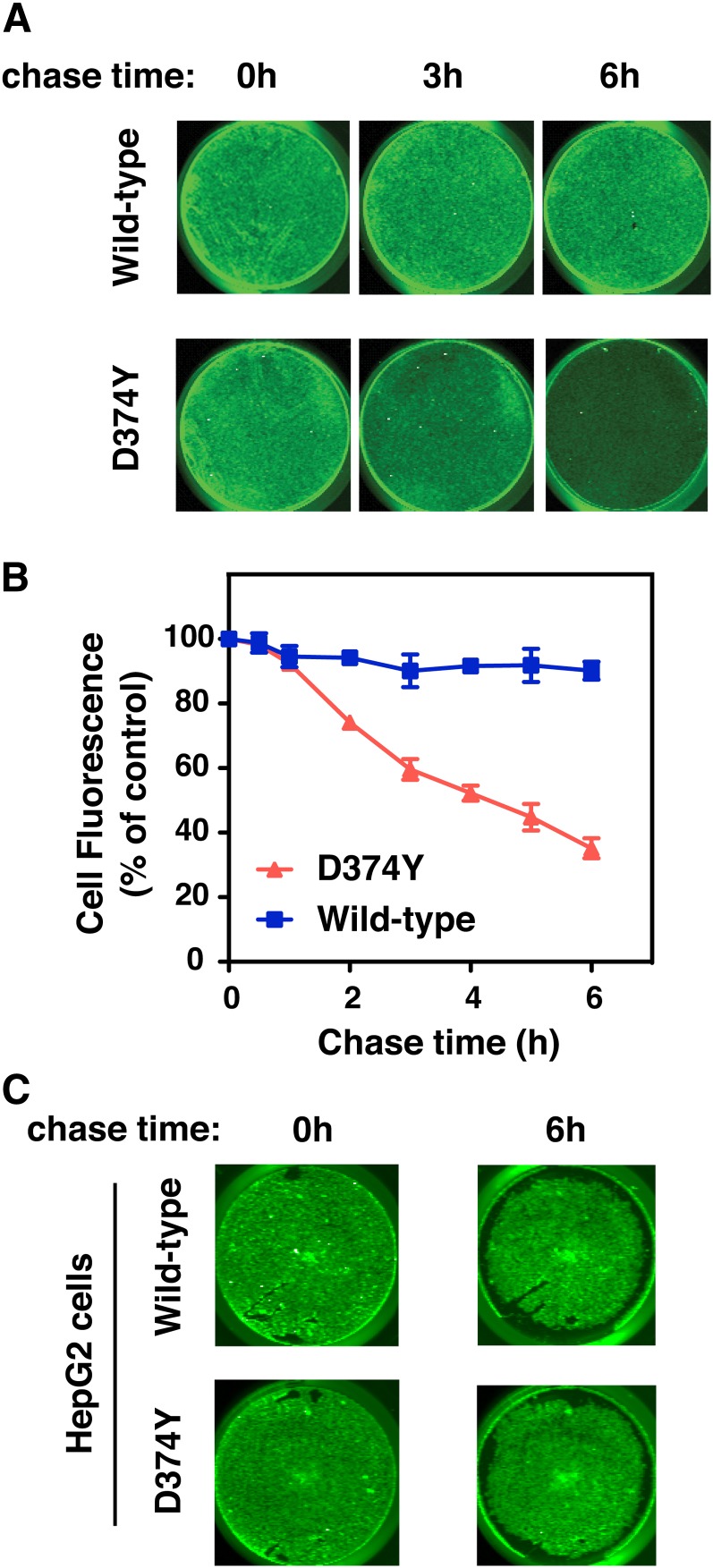
Fig. 6.
A large proportion of internalized PCSK9-D374Y recycles to the cell surface in SV-589 fibroblasts. A: SV-589 cells seeded on 24-well plates were cultured for more than 16 h in sterol-depleting Medium C in the presence of E64 (150 μM). Wild-type PCSK9 or PCSK9-D347Y covalently modified with thiol-cleavable (S-S)-biotin was preincubated with IRDye800CW streptavidin in Medium A for 1 h and added to cells for 1 h at 37°C. Labeling medium was replaced with label-free Medium A containing the noncell-permeable reducing agent TCEP (20 mM) and E64 (150 μM) and incubated at 37°C for a 6 h chase period. Plates were scanned directly on a LI-COR Odyssey infrared system at the indicated time points to measure remaining cell-associated fluorescence. Individual wells from a representative experiment are shown. B: Quantification of PCSK9-S-S-biotin-800Streptavidin recycling based on total fluorescence following continuous exposure to TCEP. Values were normalized to cell density measured using a DNA stain (DRAQ5). Results shown are expressed relative to the start of the 6 h chase period and represent the mean and standard deviation of three separate experiments. C: Lack of cell surface recycling of internalized PCSK9-D374Y in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were cultured and treated as in (A). Plates were scanned directly on a LI-COR Odyssey infrared system at the indicated time points to measure remaining cell-associated PCSK9 fluorescence. Individual wells are shown from a representative experiment repeated two other times with similar results.