Figure 15.
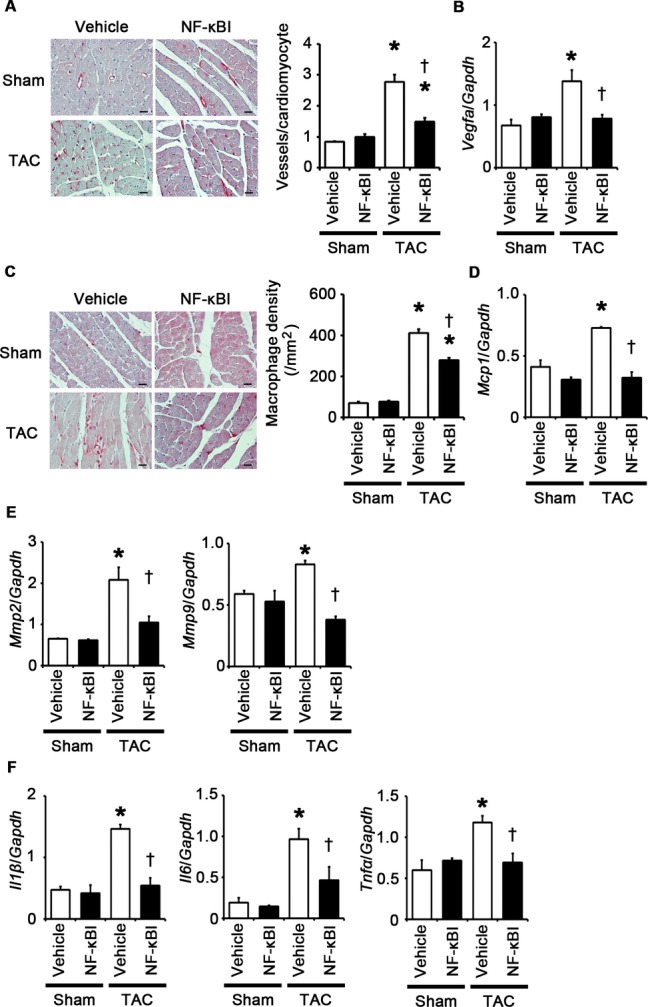
NF‐κB inhibition suppresses angiogenesis, macrophage infiltration, and expression of matrix metalloproteinases and proinflammatory cytokines at 2 weeks after TAC. A through F, Mice were analyzed at 2 weeks after TAC or sham operation under treatment of an NF‐κB inhibitor (NF‐κBI) or vehicle. A, Immunohistochemistry using antibodies to CD31. The number of vessels per cardiomyocyte was counted in 50 cardiomyocytes (n=3). Scale bars=20 μm. B, Expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (Vegfa) mRNA (n=3). C, Macrophage infiltration. Macrophage density was assessed in heart sections with anti–Mac‐3 staining (n=3). Scale bars=20 μm. D, Expression levels of monocyte chemotactic protein‐1 (Mcp1) mRNA (n=3). E, mRNA expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 (Mmp2) and 9 (Mmp9) (n=3). F, mRNA expression levels of IL‐1β (Il1β), IL‐6 (Il6), and TNF‐α (Tnfα) in the heart (n=3). Expression levels of each gene were normalized to those of GAPDH (Gapdh). *P<0.05 vs sham; †P<0.05 vs vehicle. IL indicates interleukin; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; NF, nuclear factor; TAC, transverse aortic constriction; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
