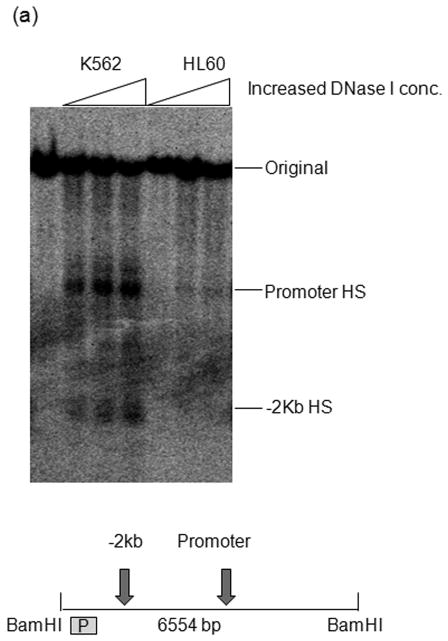
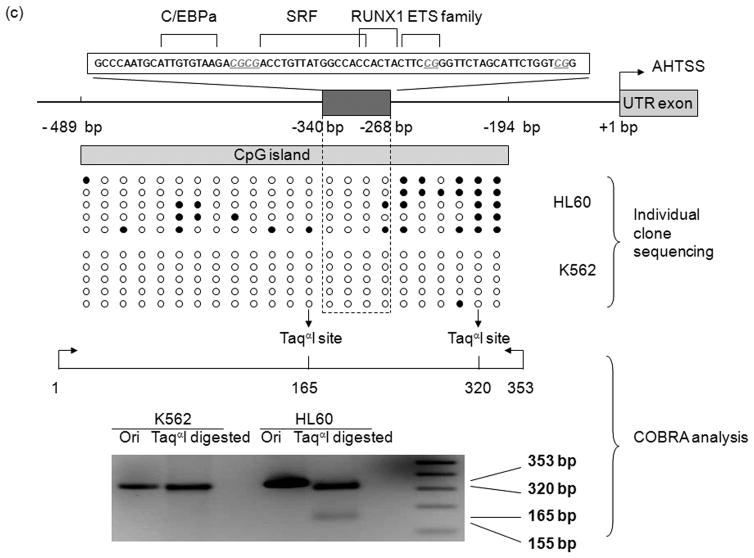
Fig. 2.
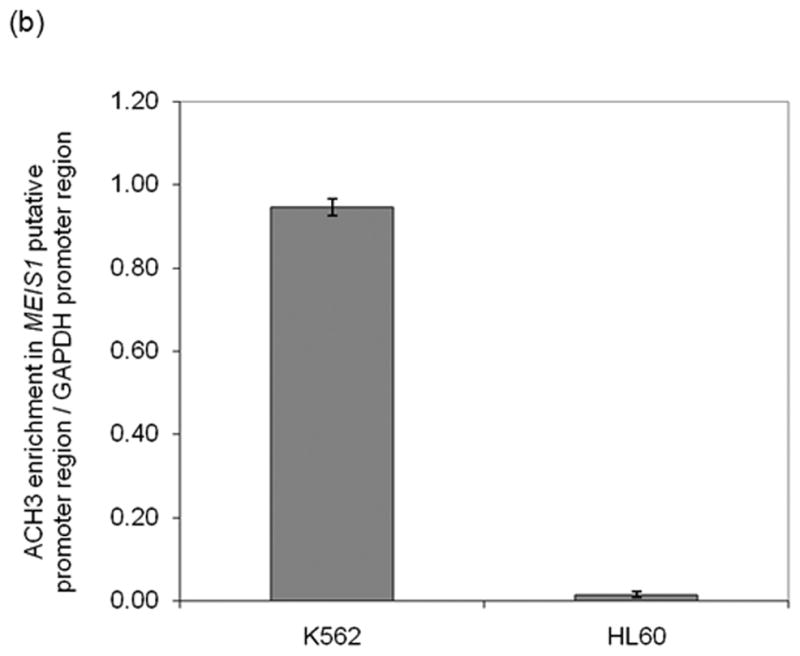
MEIS1 promoter region is accessible in MEIS1 expressing K562 cells, but not in non MEIS1 expressing HL60 cells. A) DNase I hypersensitivity assay. In K562 cells, a strong DNase I hypersensitive site (HS) was formed around MEIS1 promoter region, which was very weak in HL60 cells. B) Real time PCR results from ChIP assay with acetylated Histone H3 K9/27 antibody. MEIS1 promoter region had a similar level of acetylated Histone H3 K9/27 as the housekeeping gene GAPDH promoter region in K562, but was barely acetylated in HL60 cells. C) DNA methylation status in the CpG island of MEIS1 promoter. Ten individual clones were sent for sequencing and five unique representative clones for each cell line were shown. Open circles: unmethylated CpG; closed circles: methylated CpG. Putative transcription factor binding sites such as C/EBPα, SRF and ETS family member are shown in scale with the particular CpG sites highlighted. PCR products of the MEIS1 promoter region corresponding to 167 bp to 520 bp upstream to the AHTSS region contains two TaqαI restriction enzyme digestion sites at the 165 and 320 positions. There are more methylated CpGs in the MEIS1 promoter region in HL60 than in K562 cells as seen from both direct sequencing and COBRA analysis.