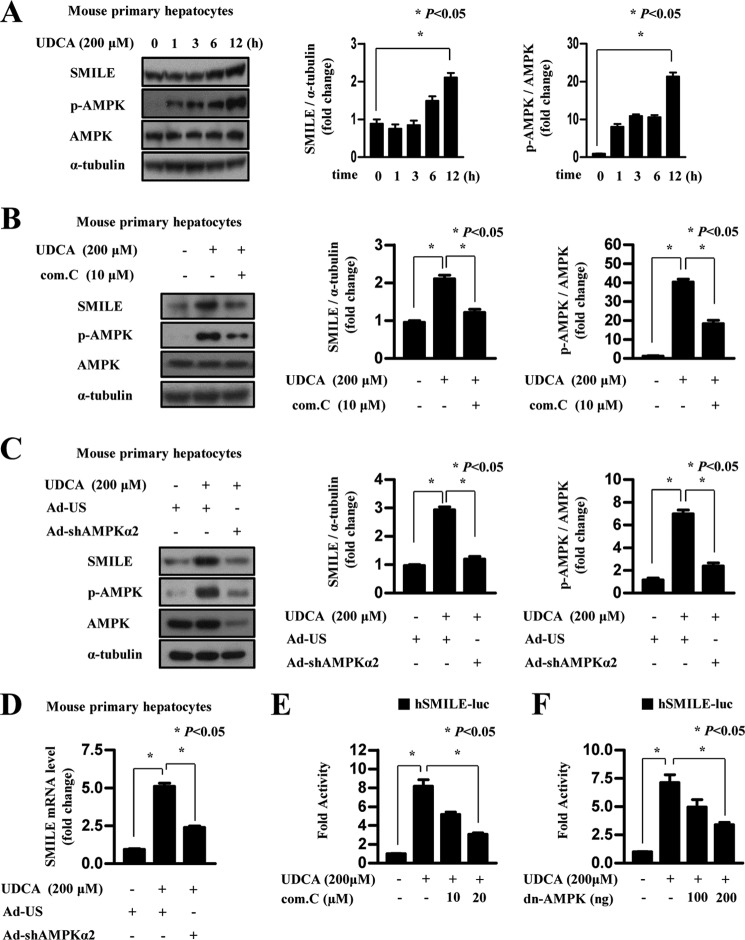
FIGURE 5.
UDCA-induced AMPK signaling elicits SMILE gene expression. A, mouse primary hepatocytes were cultured for 12 h under serum starvation. The cells were treated with 200 μm UDCA for various time periods. Whole cell extracts were isolated and analyzed using Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Protein levels were normalized to those of α-tubulin. B, mouse primary hepatocytes were co-treated for 12 h with UDCA (200 μm), compound C (AMPK inhibitor), or dimethyl sulfoxide, and then the cells were harvested for Western blot analysis. C and D, mouse primary hepatocytes cells were infected with adenovirus US (Ad-US) or adenovirus sh-AMPKα2 (Ad-shAMPKα2), and the cells treated with vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) and UDCA (200 μm). After 12 h, the cells were harvested for Western blot analysis and quantitative RT-PCR. Data represent mean ± S.D. of three individual experiments. E, HepG2 cells were transfected with 200 ng of SMILE-luc reporter vector. After 24 h, they were treated with 200 μm UDCA for 12 h with the indicated amounts of compound C (com.C). F, HepG2 cells were co-transfected with 200 ng of the SMILE-luc reporter vector and the dominant-negative AMPK expression vector. After 24 h, the cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 200 μm UDCA. The cells were harvested and lysates were utilized for luciferase and β-galactosidase assays. Data in A and B are represented as mean ± S.E.