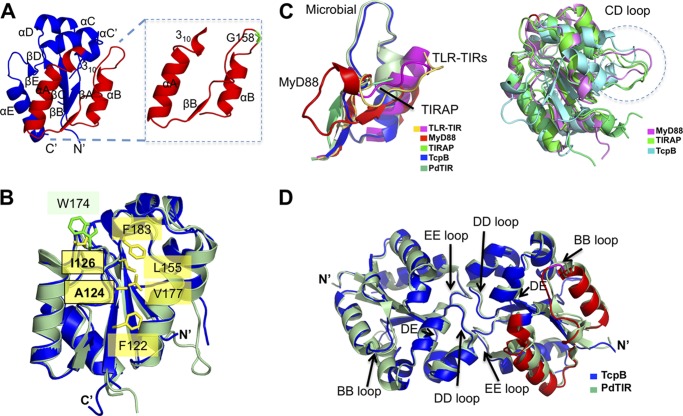
FIGURE 4.
Comparison of the TIR domain structures. A, a schematic representation of the TcpB TIR domain crystal structure is shown in blue. Inset, TcpB extended BB loop region corresponding to the microtubule-binding peptide. The Gly-158 residue important for microtubule stabilization is shown in green. B, locations of residues 124 and 126 in the TcpB structure (blue). Residue Ala-124 is located at the hydrophobic core and surrounded by residues Phe122, Val177, Leu155, and Phe183. The equivalent residue for Ile126 is Trp174 in PdTIR (pale green). Side chains for the TcpB residues are shown in yellow, and the side chains for the PdTIR residues are shown in green. C, the extended BB loop region corresponding to the microtubule-binding peptide is shown on the left, and the CD loops are shown within a dotted circle on the right. D, comparison of bacterial TIR domain dimers. Schematic representations of TIR domain dimers from TcpB (blue) and PdTIR (green) are superimposed. The loops observed at the dimer interface (DD and EE) and the BB loop important for microtubule interactions are marked.