FIGURE 4.
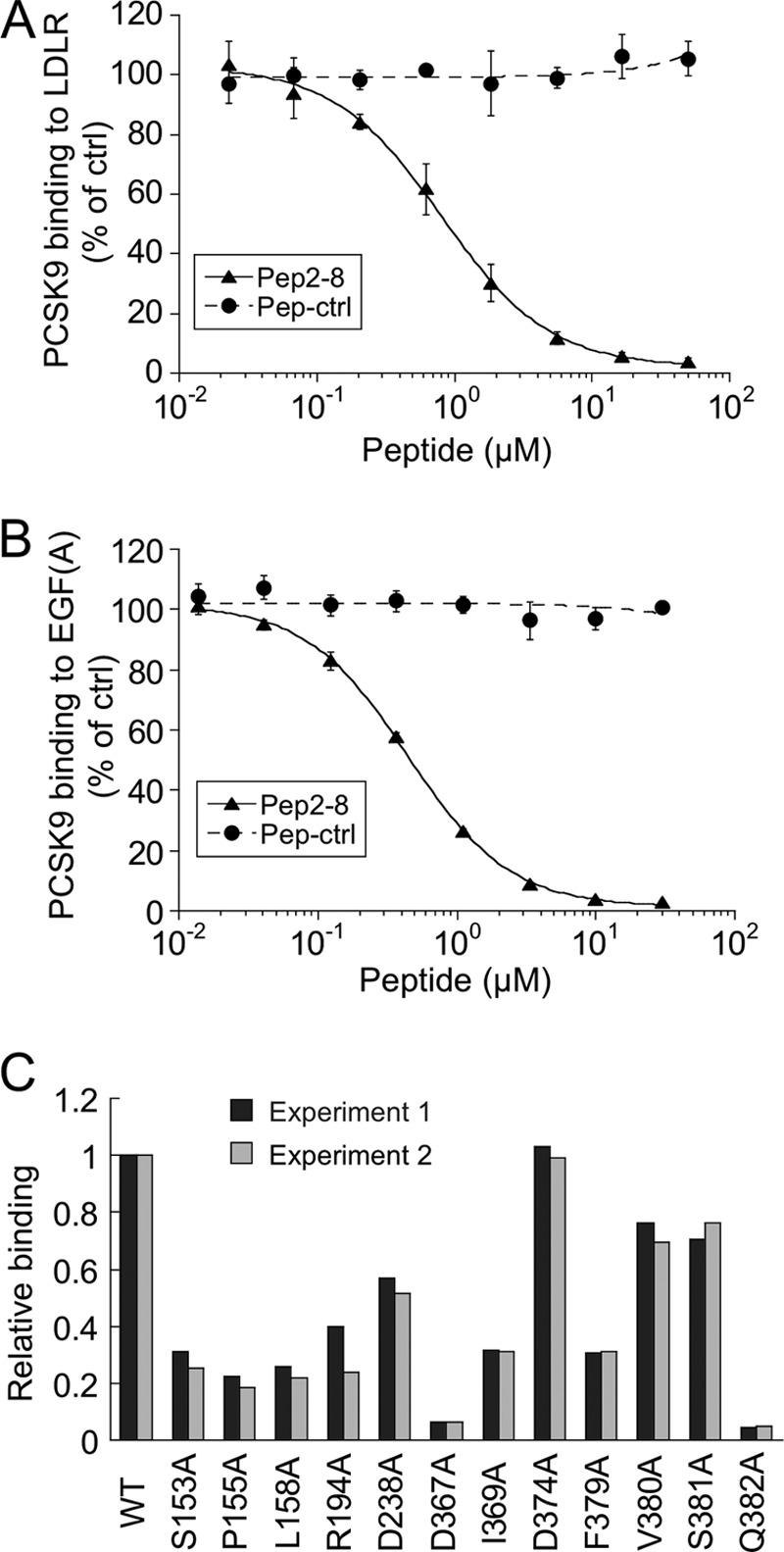
Pep2-8 competes with LDL receptor binding to PCSK9. A, inhibition of PCSK9 binding to LDL receptor. The binding of PCSK9 to plates coated with LDL receptor-Fc protein was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of Pep2-8 (filled triangles) or a control peptide (filled circles; Pep-ctrl). The IC50 calculated for Pep2-8 was 0.81 ± 0.08 μm (average ± S.D. of three independent experiments). Error bars, S.D. B, inhibition of PCSK9 binding to EGF(A)-Fc. The binding of PCSK9 to plates coated with EGF(A)-Fc protein was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of Pep2-8 (filled triangles) or a control peptide (filled circles; Pep-ctrl). The IC50 calculated for Pep2-8 was 0.44 ± 0.04 μm (average ± S.D. of three independent experiments). Error bars, S.D. C, mapping of Pep2-8 binding site by Ala scan. NeutrAvidin-coated 384-well Maxisorp ImmunoPlates were coated with biotinylated Pep2-8, and the binding of serially diluted wild type and PCSK9 mutant proteins (all with C-terminal His tag) was quantified by using HRP-conjugated anti-His antibody. The PCSK9 concentrations at 50% binding saturation (EC50) were determined and normalized to the wild type value (EC50 wild type/EC50 mutant; Relative binding). Shown are the results of two independent experiments.
