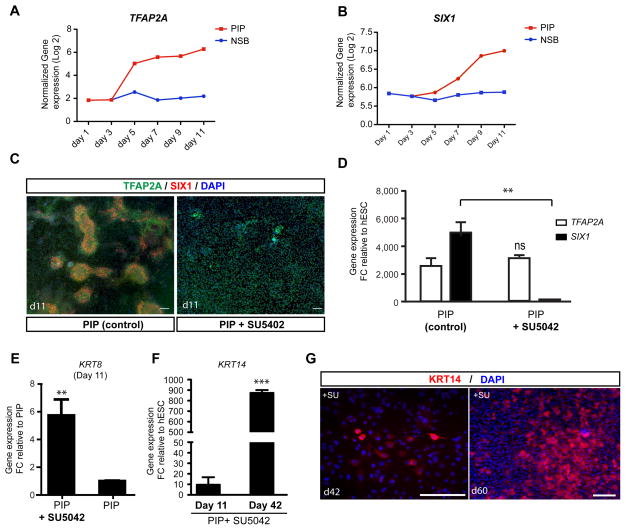
Figure 3. FGF signaling determines placodal versus non-neural ectoderm/epidermal fate (see also Figure S3).
A–B) Time course of the induction of TFAP2A and SIX1 under PIP conditions. C) TFAP2A (green) is expressed in placodes and surface ectoderm, while SIX1 (red) is only expressed in placode cells. Blocking PIP via pharmacological inhibition of endogenous FGF signaling, blocks the formation of SIX1+ cells. D) Quantification of the loss of SIX1 gene expression following treatment with the FGF inhibitor SU5402. E) Expression of early epidermal marker KRT8. Data represent fold changes of mRNA expression by qRT-PCR at day 11 compared to PIP condition. F) Expression of late epidermal marker KRT14 during keratinocyte differentiation. Data represent fold changes of mRNA expression by qRT-PCR at day 11 and day 42 compared to hESC. G) Long-term SU5402 treated cultures are expressing KRT 14 protein suggesting epidermal/keratinocyte fate. Error bar represents SD. Error bar represents SD. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001 compared with control PIP condition (n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bars in C and G correspond to 50 μm.