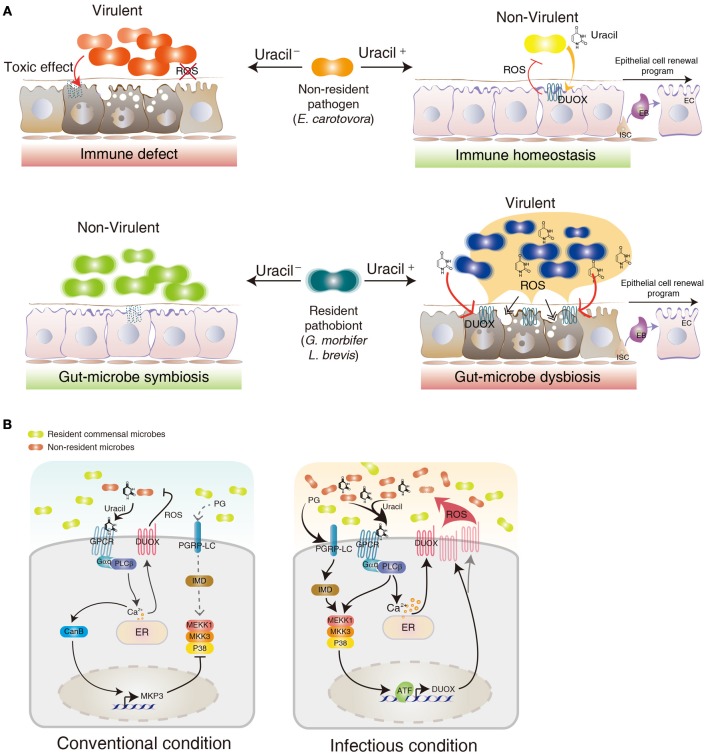
Figure 2.
Role of DUOX in gut-microbe interactions. (A) Different gut physiologies depending different uracil-releasing states (Uracil− and Uracil+ for uracil non-releasing and releasing state, respectively) and different gut-colonizing ability (resident vs. non-resident) of each bacterium in a Drosophila gut environment. (B) DUOX regulatory mechanism in conventional and infectious conditions. See text for more details.