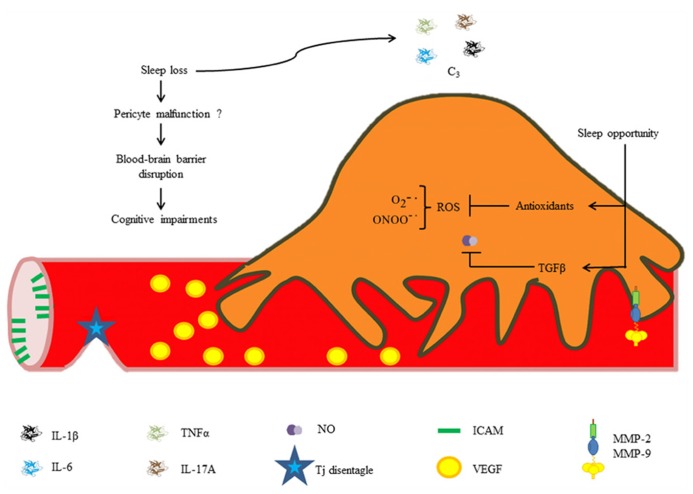
FIGURE 4.
Hypothetical roles of pericytes in REM sleep loss-induced blood–brain barrier disruption. Increased cytokine and chemokine concentrations during sleep loss may disrupt the blood–brain barrier. Brief periods of sleep opportunity may reestablish the blood–brain barrier integrity through synthesis of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TGF-β).