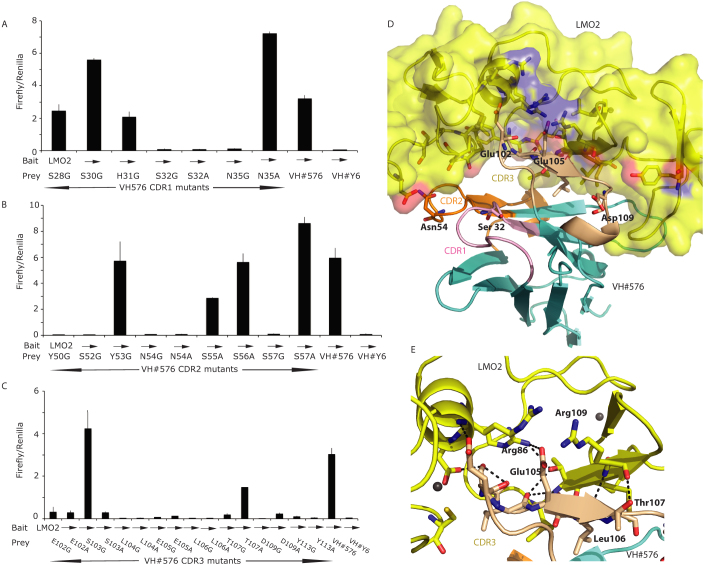
Figure 2. Probing the interaction surface of VH#576 with LMO2 using site directed mutagenesis.
The CDR residues of VH#576 were mutated to glycine or alanine and the mutant sequences cloned into pEF-VP16 vector (prey vector) for use in a mammalian two-hybrid luciferase reporter assay. These assays were performed by transient transfection into CHO cells by co-transfecting the prey vector with a vector expressing a Gal4-LMO2 fusion bait (pM1-δLMO2); luciferase signals in the histograms are the ratio of Firefly luciferase to Renilla luciferase where the latter was used as a transfection control. Controls were performed using VH#576 (positive control) and anti-RAS VH#6 (negative control). The expression levels of each mutant VH#576 protein were established by Western detection with an anti-VP16 antibody (shown at the bottom of panels A, B, C). Panel A shows data for mutations of CDR1 residues, panel B mutations of CDR2 residues and panel C mutations of CDR3 residues. Each bar represents an average of luciferase activity measured for two wells (replicates) and the bar extensions indicate the standard deviations. Panels D and E highlight the key residues in the VH#576 that emerged from the mutation analysis shown in A-C. The CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 of VH#576 are shown in salmon, orange and cream respectively. In panel D, LMO2 is shown in yellow (space filling format) and the framework region of VH in cyan, with the indicated amino acids being from the VH. Red patches are areas of oxygen atoms, blue are areas of nitrogen atoms. In panel E the interactions of VH#576 CDR3 are highlighted. A majority of the interactions occur through the CDR3 region (cream) with a total of seven CDR3 residues identified as critical for the interaction. A series of interactions occur across the hinge region (Phe88) of LMO2 including a salt bridge between Glu105 and Arg86, and polar contacts, represented by dashed lines. Zinc atoms are shown as yellow spheres.