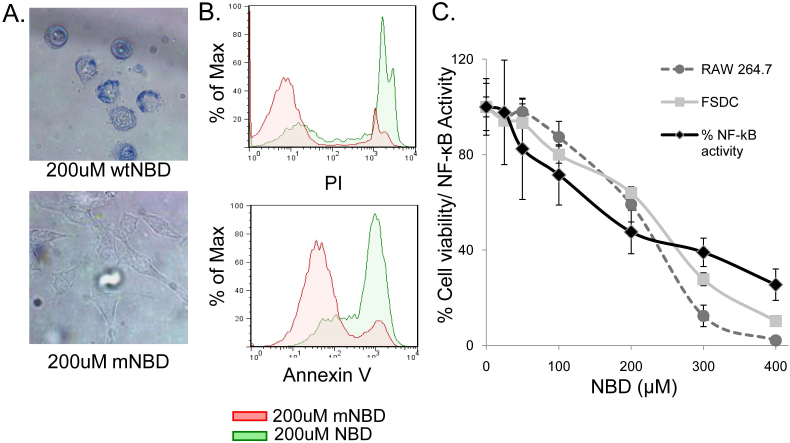
Figure 1. NBD peptide induces NF-κB inhibition-dependent cell death in APC.
(A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with TAT-NBD (NBD) or TAT-mNBD (mNBD) peptide for 12 hours, cells were then stained with trypan blue and images were obtained. The top image indicates a high number of trypan blue positive, dead cells following NBD treatment. For the bottom image, phase-contrast microscopy was utilized in order to visualize mNBD-treated cells, which remain alive and capable of excluding trypan blue. (representative of 5 independent experiments) (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated for 4 hours with NBD or mNBD peptide and analyzed for expression of Annexin V (early apoptotic marker) and PI (late apoptotic and necrotic marker) by flow cytometric analysis (representative of 3 independent experiments). (C) 293NF-κB reporter cell line was utilized to measure relative levels of NF-κB activation 2 hours after TNFα stimulation (10 ng/ml) at varying concentrations of NBD peptide (black lines). RAW264.7 macrophages (dashed line with circles) and FSDC (grey line and squares) were treated with the same doses of NBD. Percent survival was determined by MTT assay after 24 hr incubation. FSDC unlike the 293NF-κB, were not stimulated with exogenous TNFα. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments in triplicate.