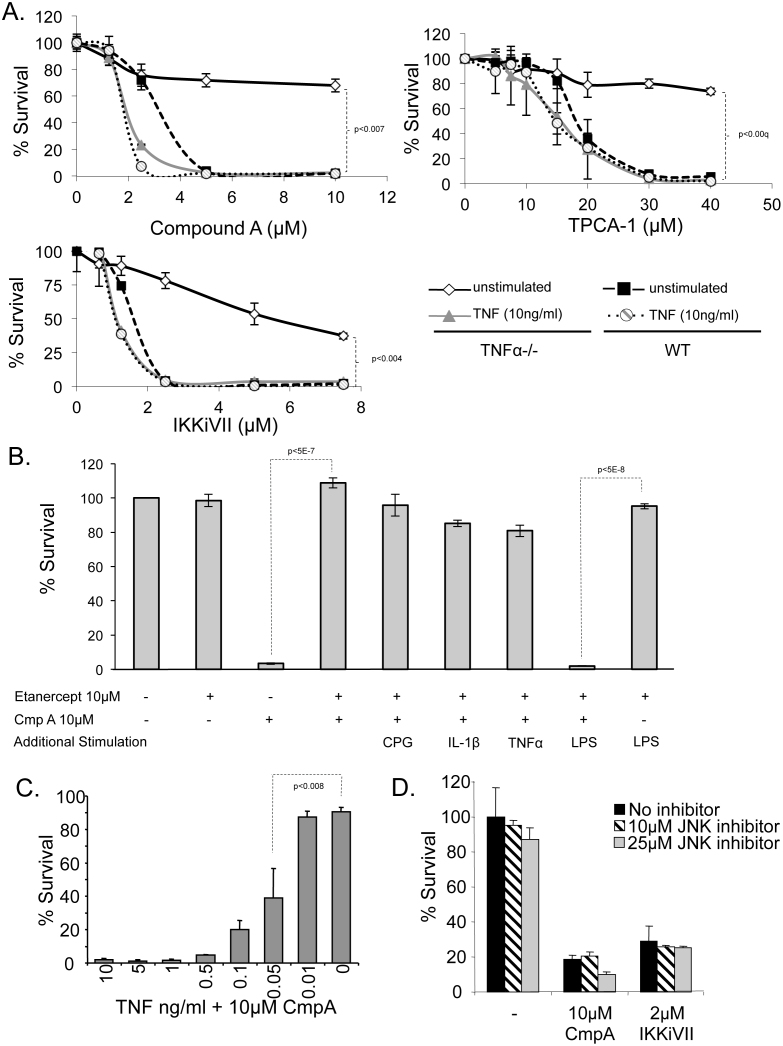
Figure 5. NF-κB-inhibition induced APC death is dependent on TNFα.
Cellular survival was measured after 24 hours using MTT assays in the following experiments: (A) TNFα−/− (dark symbols) and WT (light symbols) primary macrophages were evaluated for survival in the presence of NF-κB inhibitors in unstimulated cells (blue) or following stimulation with 10 ng/ml of TNFα (red). (statistical variation was evaluated at max concentration using ANOVA analysis) (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated with etanercept (25 ng/ml) and compound A (10 μM) in the presence of several endogenous and exogenous known NF-κB activators, CpG (7 ng/ml), IL-1β (10 ng/ml), TNFα (10 ng/ml) and LPS (100 ng/ml). MTT assay was used to evaluate survival after overnight incubation. Controls included untreated RAW264.7 cells, etanercept treatment alone, and etanercept + LPS treatment. Representative results are from at least 3 independent experiments in triplicate (p-values determined by student T-test). (C) TNFα−/− macrophage survival was measured by MTT assay in the presence of 10 μM Compound A and varying concentrations of TNFα. Addition of 0.05 ng/ml TNFα led to significant (p<0.008) cell death compared with untreated cells using a student t-test. (D) Cell survival was determined by MTT assay for FSDC pretreated with either 10 or 25 μM of specific JNK inhibitor (SP600125) and in the presence of three NF-κB inhibitors. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments in triplicate.