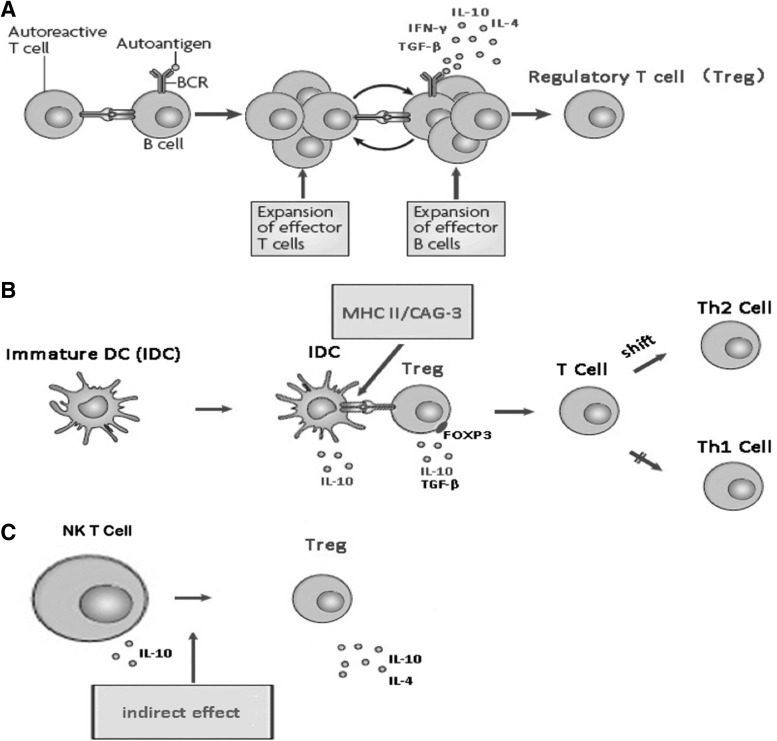
FIG. 1.
The intercommunication of the regulatory T cells, DCs, and NKT cells. (A) The initiation of cognate interactions between autoreactive T and B cells and the establishment of a B and T cell-dependent reaction, the production of cytokines (eg, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, TGF-β, etc.) were involved, in turn promoting the activation of Treg. (B) The production of Treg or effector T lymphocytes induced by DCs depended on the immature status, referring to the ratio of immature DCs and mature DCs. Cytokines released by regulatory DCs (immature DCs) might affect the immune activity, and exert immunoregulatory effects. (C) NKT cells possess more similarities to Tregs than other cells. The activation of NKT cells was directly enhanced by certain ligands, but also indirectly through activation of Tregs by cytokines secretion, and NKT cells influenced other T cell functions via regulation of their cytokine responses. DC, dendritic cell; NKT cell, natural killer T cell; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; Tregs, regulatory T cells; IL, interleukin.