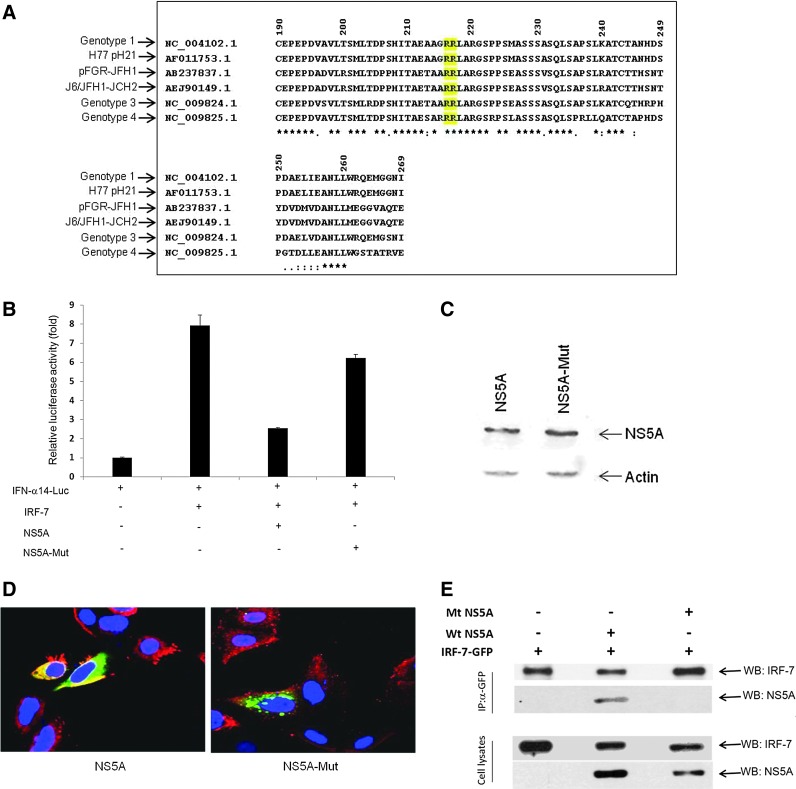
FIG. 3.
NS5A Arg216 and Arg217 are critical for inhibition of IRF-7-mediated IFN-α14 promoter activation. (A) Alignment of partial NS5A sequences from amino acid residues 190–269 among different genotypes is shown. The sequence analyses displayed conserved arginine residues marked in yellow. (B) IHH were cotransfected with human IFN-α14-luc reporter plasmid, IRF-7, and wild-type or mutant HCV NS5A constructs. The luciferase activity was measured 48 h post-transfection. Results presented are mean with standard error from 4 independent experiments. Empty vector DNA was used as a negative control and mean basal value was arbitrarily set at 1. (C) HCV NS5A (wild-type or mutant) protein expression is shown by immunoblotting with the FLAG antibody for detection of the NS5A protein. (D) IHH were cotransfected with IRF-7-GFP and wild-type or mutant HCV NS5A. Cells were stained after 48 h of transfection for expression of NS5A (red) and IRF-7 (green). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Cytoplasmic localization of IRF-7 and NS5A was observed from images superimposed digitally for fine comparisons in confocal microscopy. (E) IRF-7-GFP plasmid DNA was cotransfected with wild-type NS5A (Wt NS5A) or mutant NS5A (Mt NS5A) into 293 cells. Cell lysates were prepared after 48 h of transfection and immunoprecipitated with the anti-GFP antibody. Association of IRF-7 and wild-type or mutant NS5A was detected by immunoblotting with specific antibodies.