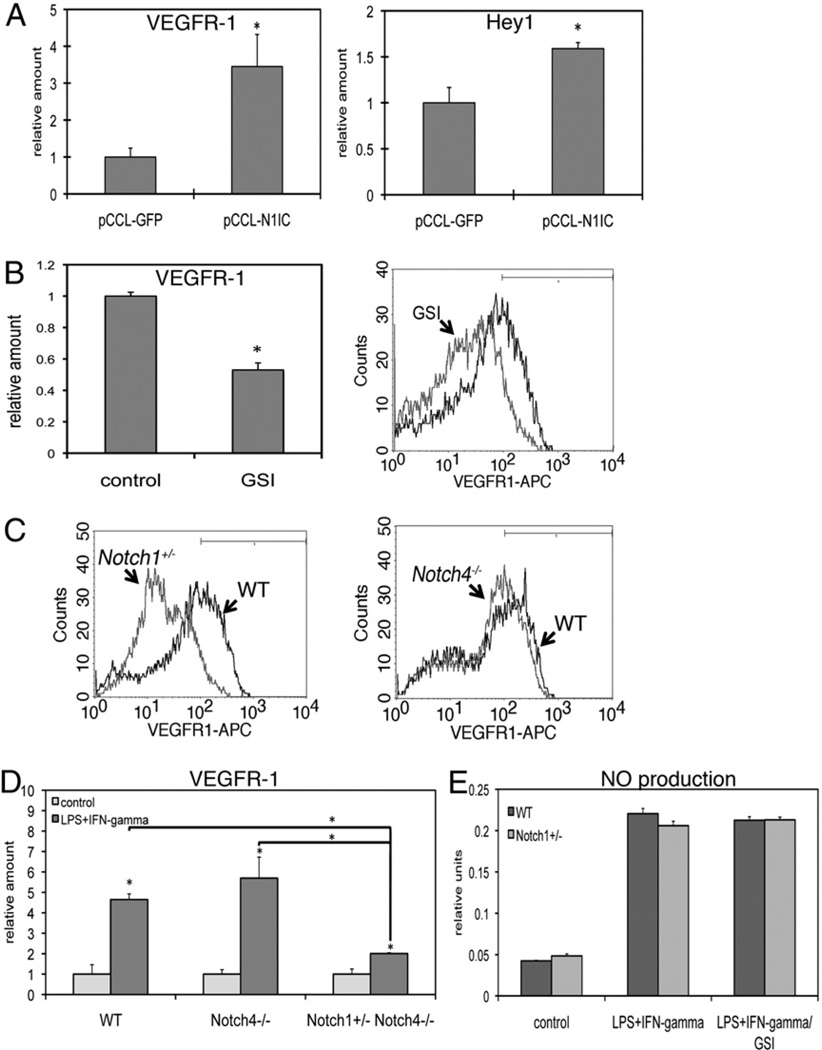
FIGURE 7.
Notch1, not Notch4, regulates baseline levels of VEGFR-1 in BMM. A, A lentiviral construct encoding the constitutively active N1IC was transduced into BMM and transcripts were assessed by quantitative RT-PCR 48 h postinfection. N1IC trans-duction led to increased VEGFR-1 expression (left), as well as increased expression of the Notch target gene Hey1 (right). B, Incubation of resting BMM with GSI overnight led to decreased transcript (left) and protein (right) levels of VEGFR-1. C, BMM from Notch mutant mice were analyzed for VEGFR-1 expression by flow cytometry. Notch1+/− BMM had decreased surface expression of VEGFR-1 (left), whereas VEGFR-1 expression in Notch4−/− BMM was largely unchanged (right) compared with WT BMM. D, Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrated that BMM from Notch4−/− mice induce VEGFR-1 in response to LPS/IFN-γ to a similar degree as do WT BMM, whereas loss of Notch1 leads to diminished induction of VEGFR-1. E, Production of NO in culture supernatant from WT or Notch1+/− BMM was assessed by Griess reagent. Cells were stimulated overnight with LPS/IFN-γ. Some cells were coincubated with GSI. Quantitative RT-PCR results represent reactions performed in triplicate and normalized to expression of P0 (±SD). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 relative to control. WT, wild-type.