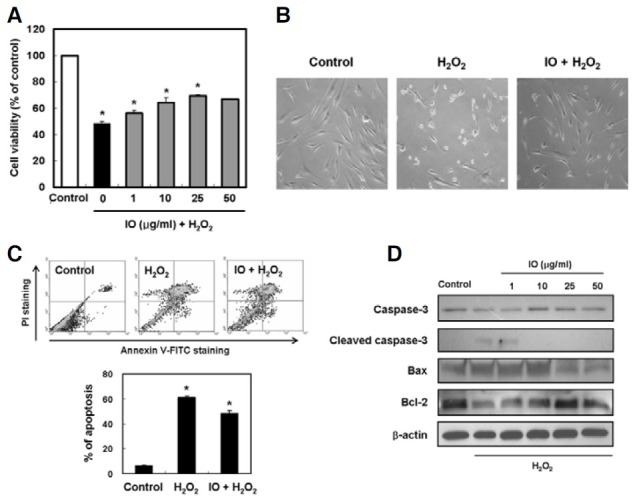
Fig. 2. Effect of I. obliquus on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human dermal fibroblasts. (A) Protective effect of I. obliquus against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide was determined using the MTT assay. (B) Representative micrographs of hydrogen peroxide-induced morphological changes in cells treated with or without 1 mM hydrogen peroxide and 25 μg/ml I. obliquus extract. Magnification: 100-fold. (C) The number of apoptotic cells was detected by the annexin V/PI flow cytometry analysis. The cells were treated with or without 25 μg/ml I. obliquus extract for 4 h prior to the addition of 1 mM hydrogen peroxide. Data (A and C) represent the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. Significant differences were compared with the control at *p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (D) Altered expression of apoptotic-related proteins in cells treated with or without 25 μg/ml I. obliquus extract for 4 h prior to the addition of 1 mM hydrogen peroxide. The levels of caspase 3, Bax, and Bcl-2 were assessed using Western blot analysis. Equal loading of total proteins in each sample was verified by β-actin expression.