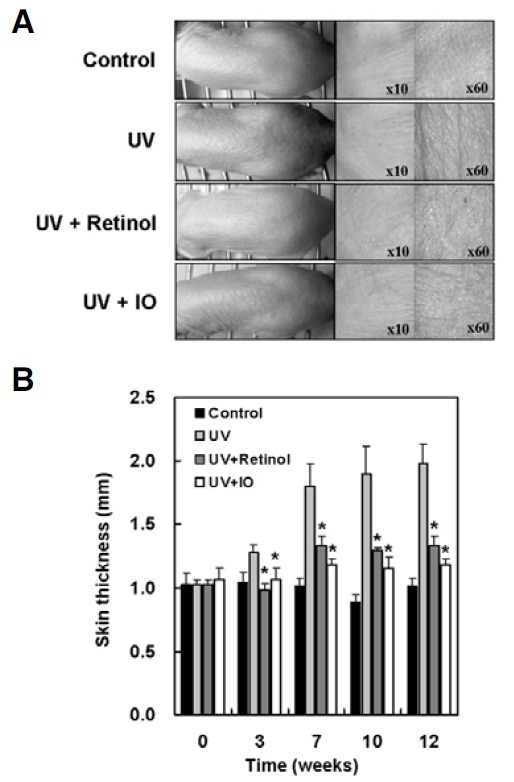
Fig. 5. Effect of I. obliquus on UV irradiation-induced wrinkle formation and skin thickening in hairless mice. UV irradiation exposed three times a week for 12 weeks in the back skins of hairless mice. After UV exposure, retinol (0.5%), vehicle alone or I. obliquus extract (1.0%) were applied. (A) Photodamaged dorsal skin (wrinkle formation area) was photographed by a skin diagnosis system. Magnification: 10-fold or 60-fold. (B) Skin thickness was measured midway between the neck and hips with a caliper every week. Data represents the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. Significant differences were compared with the UV control at *p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test.