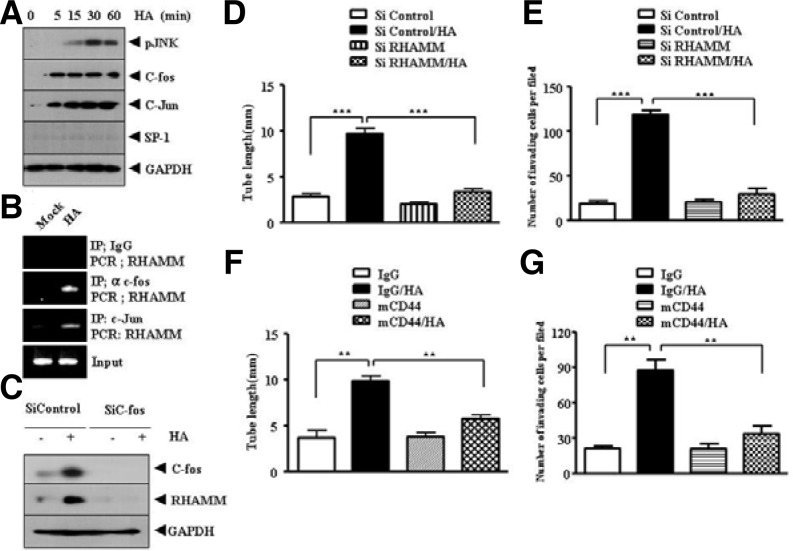
Fig. 3.
RHAMM, induced by HA via AP-1, and CD44 mediate HA-promoted angiogenesis. (A) HUVECs were treated with or without HA (1 mDa, 200 μg/ml) for various time intervals. Western blot analysis was performed. (B) HUVECs were treated with or without HA (1 mDa, 200 μg/ml) for 1 h and ChIP assays using anti-IgG (2 μg/ml), anti-c-jun (2 μg/ml) or anti-c-fos antibody (2 μg/ml) was performed. (C) HUVECs were transfected with control SiRNA (10 nM) or c-fos SiRNA (10 nM). At 48 h after transfection, cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis. (D) HUVECs were transfected with control SiRNA (10 nM) or RHAMM SiRNA (10 nM). At 48 h after transfection, HUVECs were then treated with or without HA (1 mDa, 200 μg/ml). Endothelial cell tube formation assays were performed as described. Means ± SEM of three independent experiments are depicted. ***p < 0.0005. (E) is the same as (D) except that cellular invasion assays were performed as described. The trypsinized HUVECs (2 × 104 cells) were subjected to transwell migration assays as described. Means ± SEM of three independent experiments are depicted. ***p < 0.0005. (F) HUVECs were pre-incubated with IgG antibody (5 μg/ml) or CD44-blocking antibody (A3D8, 5 μg/ml) for 3 h, followed by treatment with or without HA (200 μg/ml). Endothelial cell tube formation assays were performed 12 h after addition of HA (left panel). Effect of blocking of CD44 on the invasion potential of HUVECs was also determined as described (right panel). Means ± SEM of three independent experiments are depicted. **p < 0.005.