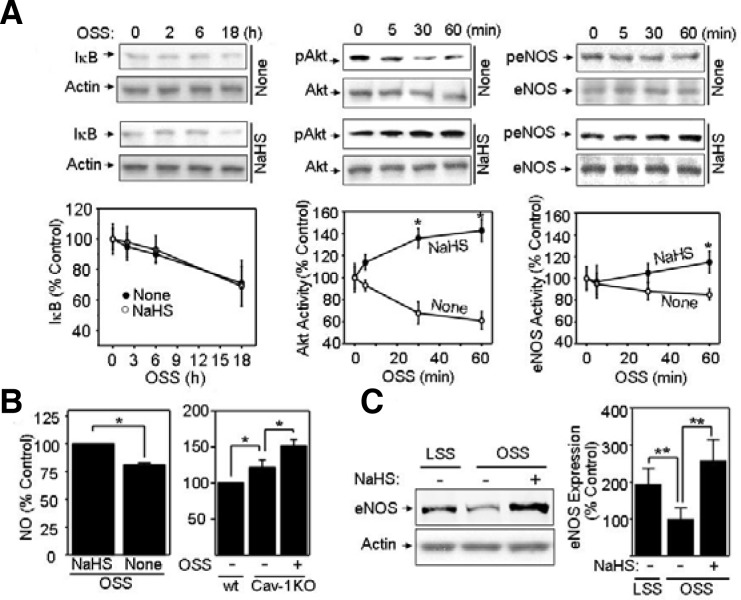
Fig. 3.
NaHS stimulates activation of Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and enhances eNOS expression. (A) Bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) pretreated with 1 mM NaHS or none were exposed to oscillatory shear stress (OSS) (± 5 dyn/cm2). Then, cells were analyzed for IκB, p-Akt, and pS1177-eNOS by Western blotting. The blots were probed with antibodies specific for IκB, total or p-Akt, and total or pS1177-eNOS. Quantification was performed using densitometry and data are plotted as line graphs shown in the lower panels (mean ± standard error [SE], n = 3). *P < 0.05 (B) BAECs were treated with none or 1 mM NaHS under acute (1 h) OSS (left panel). Wild-type (wt) or caveolin-1 knocked-out (Cav-1 KO) MAECs were exposed to none or OSS (right panel). Then, cells were pre-incubated with HEPES buffer containing 1 μmol/L Ca2+ ionophore, A23187, for 20 min and incubated with 0.1 μmol/L DAF-2 for 15 min. Finally, intracellular NO was measured as described in “Materials and Methods”. Data are plotted as bar graphs (mean ± SE, n = 3). *P < 0.05 (C) BAECs were pretreated with none or 1 mM NaHS followed by LSS or OSS for 24 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-eNOS antibody. Equal amounts of protein loading were shown by probing the blot with anti-actin antibody. Quantification was performed using densitometry, and data are plotted as bar graphs (mean ± SE, n = 3). **P < 0.03.