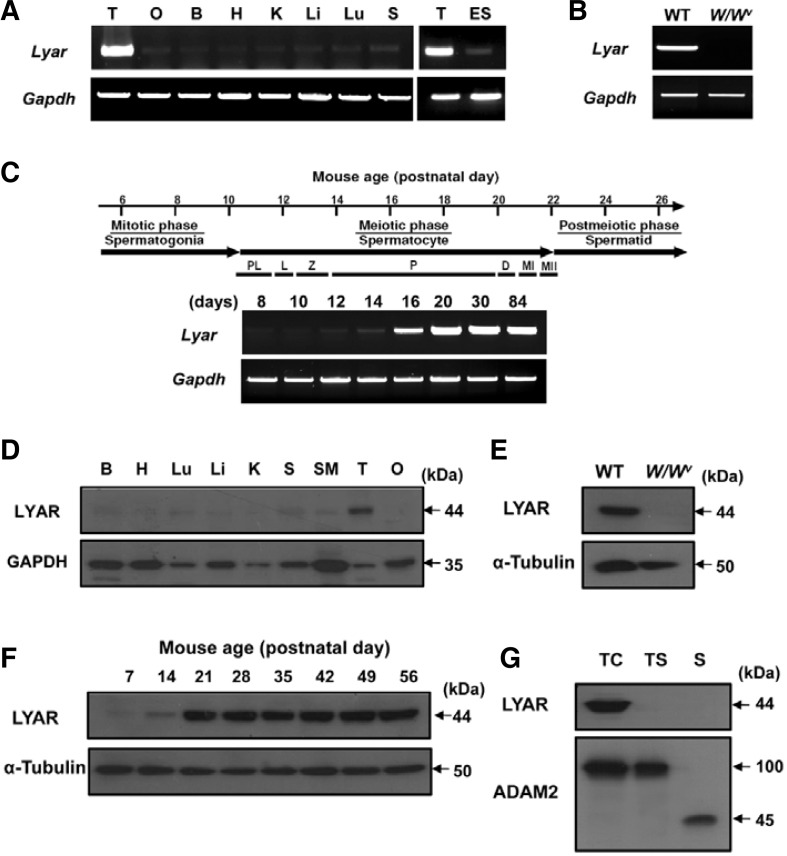
Fig. 1.
The expression pattern of Lyar. transcripts and proteins. (A) The expression pattern of Lyar in various mouse tissues was determined by RT-PCR. Gapdh was included as a loading control. Abbreviations: T, testis; O, ovary; B, brain; H, heart; K, kidney; Li, liver; Lu, lung; S, spleen; ES, embryonic stem cells; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (B) Germ cell-specific expression of Lyar. RT-PCR was performed using testes from wild-type (WT) and germ cell-lacking W/Wv. mice. (C) Developmental expression pattern of Lyar. Juvenile spermatogenesis consists of the mitotic, meiotic, and postmeiotic phases. Stage-specific expression of Lyar was determined from mouse testes on different postnatal days (8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20, 30, and 84 days). Abbreviations: PL, preleptotene; L, leptotene; Z, zygotene; P, pachytene; D, diplotene; MI, meiotic division I; MII, meiotic division II. (D) Tissue distribution of the LYAR protein. An anti-GAPDH antibody was used as a control. B, brain; H, heart; Lu, lung; Li, liver; K, kidney; S, spleen; SM, smooth muscle; T, testis; O, ovary. (E) The LYAR protein in WT and W/Wv testes. Total testicular lysates from WT and germ cell-lacking W/Wv mutant mice were immunoblotted with the anti-LYAR antibody. An anti-α-tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. (F) Developmental expression of LYAR during spermatogenesis was determined by immunoblotting using total testis lysates obtained from prepubertal and adult male mice of various postnatal ages (7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, and 56 days). (G) Stage-specific expression of LYAR. Protein samples from testicular cells (TC), testicular sperm (TS) and epididymal mature sperm (S) were immunoblotted with the anti-LYAR antibody. ADAM2 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease 2) protein, showing the 100 kDa-precursor and 45 kDa-processed forms, was included as a reference protein.