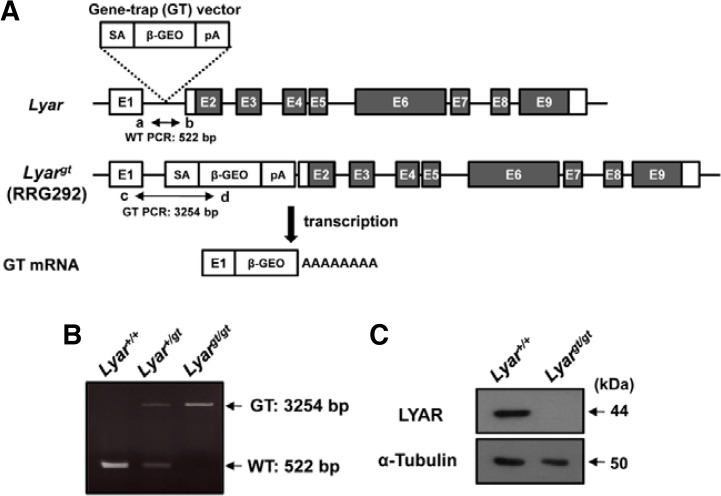
Fig. 3.
Generation of Lyar mutant mice. (A) Schematic diagram of the Lyar gene and gene-trap vector insertion. The numbers in the boxes represent exons and the filled boxes indicate the coding regions of LYAR. The gene-trap construct contains a splicing acceptor sequence (SA), β-galactosidase-neomycin resistance fusion gene (β-geo), and polyadenylation signal (pA). Arrows show the primers (a, b, c, and d) used in (B). Abbreviations: WT, PCR from wild-type allele; GT, PCR from allele with gene-trap mutation. (B) PCR genotyping analysis using the allele-specific primers shown in (A). Amplification with primers a and b (WT allele) yielded a 522-bp PCR product, and amplification with primers c and d (GT allele) yielded a 3254-bp PCR product. (C) Deficiency of LYAR expression in Lyar mutant testes. Testicular samples from WT (Lyar+/+) and Lyar mutant mice (Lyargt/gt) were immunoblotted with an antibody against LYAR. An anti-α-tubulin antibody was included as a control for sample loading.