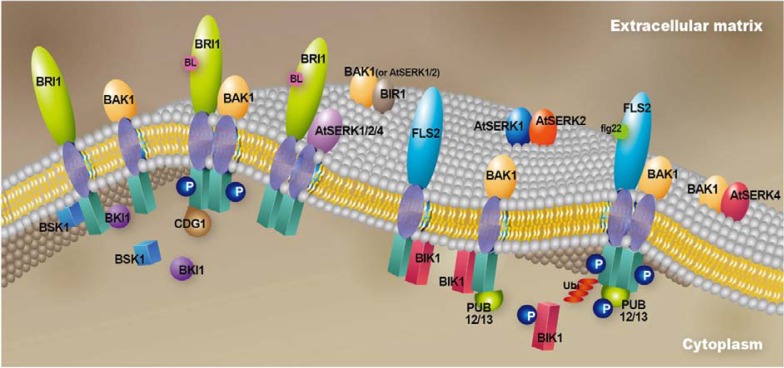
Fig. 2.
Various receptor complexes containing BAK1 or AtSERK proteins exist in the vicinity of plasma membrane. Binding of BL to BRI1 triggers the release of BKI1 from BRI1 and recruits BAK1 to form a complex. The subsequent sequential phosphorylation fully activates the kinase activities of BRI1 and BAK1, and BRI1 phosphorylates BSK1 and CDG1. BRI1 forms complexes with AtSERK1, AtSERK2 and At-SERK4. Cytoplasmic kinase BIK1 interacts with both FLS2 and BAK1 separately on the plasma membrane under steady-state conditions. PUB12 or PUB13 are bound to BAK1. Flagellin pulls the FLS2/BIK1 and BAK1/BIK1 complexes together to form FLS2/BAK1/BIK1/PUB13. Transphosphorylation between these proteins results in the release of BIK1 from FLS2 and the polyubiquitination of FLS2 through PUB13. Another complex consisting of BAK1 and BIR1 together with cytoplasmic BON1 or BON3 is also localized on the plasma membrane. BIR1 also interacts with AtSERK1 and AtSERK2. These complexes are involved with the repression of ETI in the absence of pathogen effectors. Complex formation between the AtSERK1 proteins, AtSERK1 and AtSERK2 in male reproductive organ development, and an association of the AtSERK3/AtSERK4 complex with cell death control have been assumed, although direct evidence has not been reported.