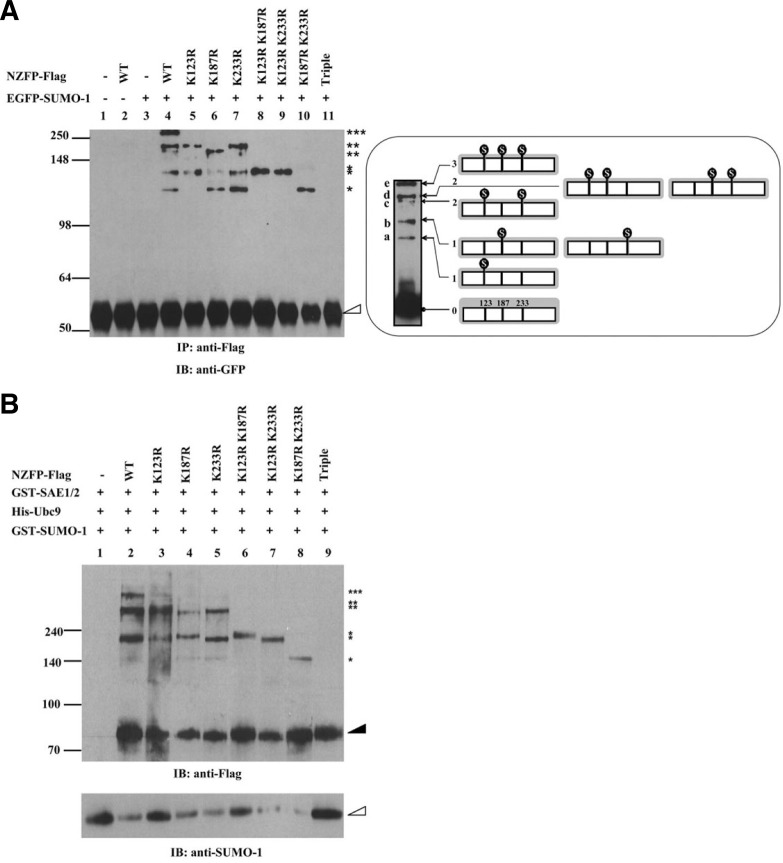
Fig. 2.
NZFP is sumoylated at three consensus SUMO acceptor sites. (A) In vivo sumoylation assay of NZFP and its mutant derivatives. Flag fused wild type or mutant NZFP constructs were co-transfected with pGFP-SUMO-1 into 293T cells. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and the bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-GFP antibody (left) as the primary antibody. Asterisks designate the number of SUMO-1 bound to each NZFP. The empty triangle designates immunoglobulin heavy chain. IP and IB designate immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting, respectively. The right panel shows the position of SUMO-1 bound to NZFP (indicated by
 ) and the band produced by each SUMO-1/NZFP complex. Ovoid structure represents SUMO-1 bound to NZFP. (B) In vitro sumoylation of NZFP and its mutants. The proteins described on the top were expressed in E. coli, purified and subjected to the in vitro sumoylation assay. Asterisks represent the number of SUMO-1 bound to each NZFP or its mutants. Solid and empty triangles designate NZFP-Flag and GST-SUMO-1, respectively.
) and the band produced by each SUMO-1/NZFP complex. Ovoid structure represents SUMO-1 bound to NZFP. (B) In vitro sumoylation of NZFP and its mutants. The proteins described on the top were expressed in E. coli, purified and subjected to the in vitro sumoylation assay. Asterisks represent the number of SUMO-1 bound to each NZFP or its mutants. Solid and empty triangles designate NZFP-Flag and GST-SUMO-1, respectively.