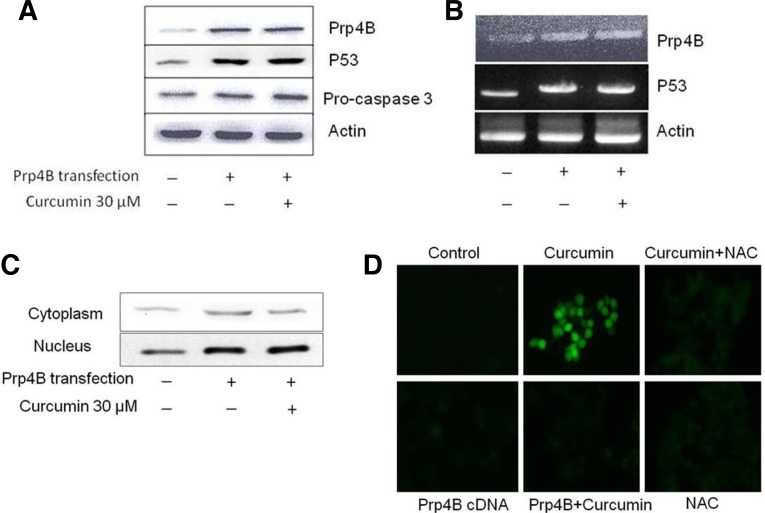
Fig. 4.
Exogenous expression of Prp4B restricts curcumin-induced apoptosis in HCT-15 cells. (A) Effect of Prp4B stably transfected cells by Western blotting. HCT-15 cells were transfected with Prp4B clone and total protein was isolated from cells and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Prp4B and anti-actin antibodies. (B) Prp4B expression inhibits curcumin-induced apoptosis in HCT-15 cells. Cells were transfected with Prp4B clone and then incubated with 30 μM curcumin, total protein was isolated from cells and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Prp4B, -p53, pro-caspase-3, and -actin antibodies. (C) Prp4B translocates from the cytosol to the nucleus. Transfectant HCT-15 cells were treated with curcumin for the indicated time. Cells were fractionated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions and equal amounts of lysates were used for immunoblotting with Prp4B-specific anti-bodies. (D) Prp4B expression decreases ROS generation. HC-T15 cells were transfected with Prp4B clone or NAC and then incubated with curcumin or carrier for the indicated time. Prp4B over-expression and NAC treatment diminished curcumin-induced ROS generation as shown by DCFHDA fluorescence.