Fig. 1.
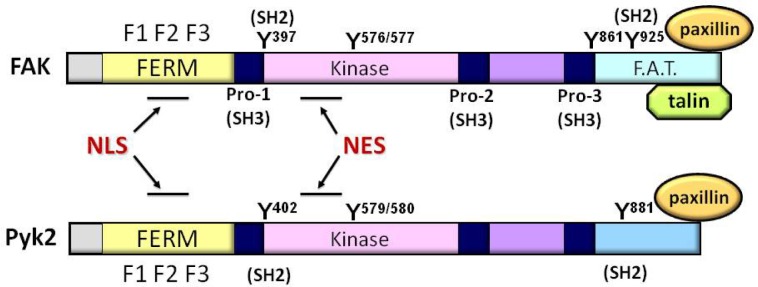
Schematics of FAK and Pyk2. FAK and Pyk2 have a conserved central kinase domain (amino acid homology 60%). Both proteins contain a unique N-terminal FERM (band 4.1, ezrin, radixin, and moesin homology) domain which consists of three subdomains, F1, F2, and F3. FAK C-terminal domain, also called as focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain, is indirectly linked to integrin adhesomes by interacting with major focal adhesion components such as talin and paxillin, while the Pyk2 C-terminus does not have a binding motif for talin and is shorter than the FAK C-terminus by ∼50 amino acids. In both FAK and Pyk2, the nuclear localization sequence (NLS) is located within F2 domain of FERM, and the nuclear export signal (NES) is also well conserved in the kinase domains. There are three proline-rich domains providing the binding sites for Src homology 3 (SH3) domain-containing proteins such as p130Cas. FAK has five major tyrosine (Y) phosphorylation sites (Y397, Y576, Y577, Y861, and Y925). Y576/Y577 serves as the activation loop and tyrosine phosphorylation of Y397 autophosphorylation or Y925 sites can provided the binding site for Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing proteins such as Src tyrosine kinase or Grb2. Pyk2 has the equivalent autophosphorylation site at Y402 for providing Src binding motif, the activation loop Y579/Y580 and the C-terminally located SH2 containing-protein binding site at Y881.
