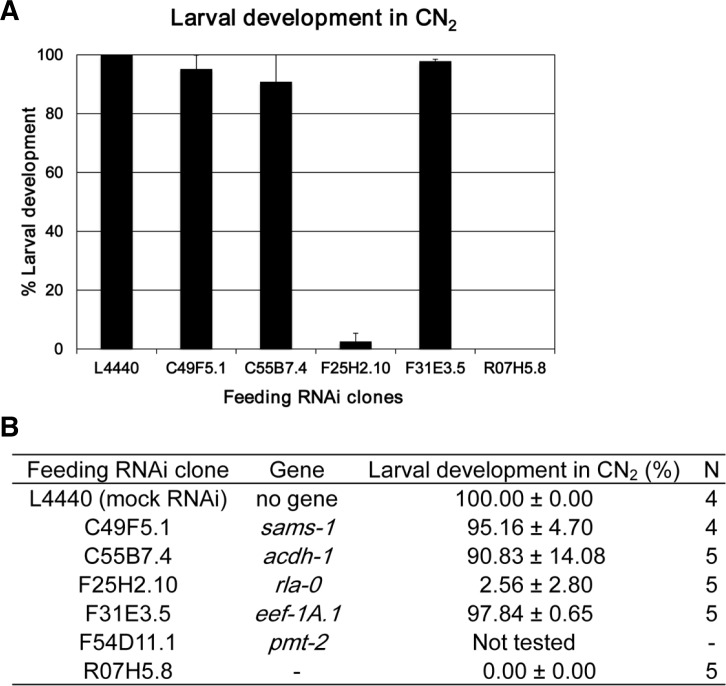
Fig. 2.
Percent larval development of worms treated with RNAi against CS down-regulated genes for two generations in CN condition. Synchronized L1 wild-type N2 worms were grown on CN plates seeded with bacterial clones for feeding RNAi against five of the six genes that were down-regulated in CS until the L4 stage (first generation), and these L4 worms were individually transferred to respective fresh feeding RNAi plates for three to four consecutive days until they finish laying self-fertilized eggs. Then, percent larval development of hatched progeny (second generation) after each feeding RNAi was collectively scored and displayed as a bar graph (A) and summarized as a table (B). Error bars in (A) show S.D. N in (B) is the number of L4 mother worms used to measure percent larval development of their progeny after each RNAi. F54D11.1 (pmt-2) was not tested. L4440 was used as a mock feeding RNAi control.