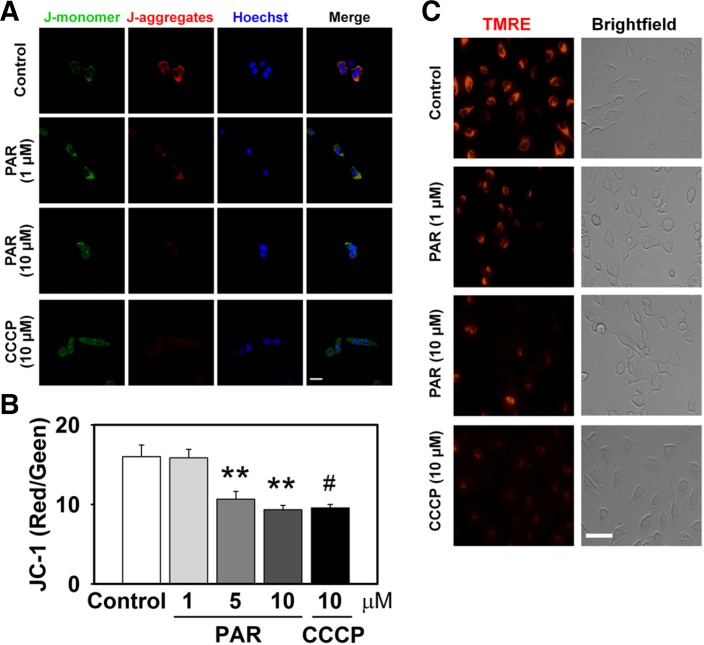
Fig. 2.
PAR polymer depolarizes mitochondrial membrane potential in cells. HeLa cells were treated with PAR polymer for 3 h at 37°C. After replacement with fresh media, cells were labeled for imaging. CCCP was applied 30 min before labeling. (A) Confocal microscope images of PAR polymer-treated HeLa cells after staining with JC-1. Cells were labeled with JC-1 and visualized by confocal microscopy after counter staining of nuclei with Hoechst 33342 (scale bar represents 20 μm). JC1 (mono), JC-1 in monomeric form; JC1 (aggre), JC-1 in aggregate form. (B) Fluorometric analysis of PAR polymer-treated HeLa cells after staining with JC-1. Fluorescent intensity of J-aggregates (red) and Jmonomers (green) in cells stained with JC-1 were measured using a fluorescence microplate reader. Bar represents ratio of red to green intensity (mean ± SEM). Significant difference to control was determined by one-way ANOVA (Duncan’s multiple range test, **P < 0.01) or t-test (#P < 0.05). (C) Fluorescence microscope images of PAR polymer-treated HeLa cells after staining with TMRE. Cells were labeled with TMRE and visualized by fluorescence microscopy (scale bar represents 100 μm).